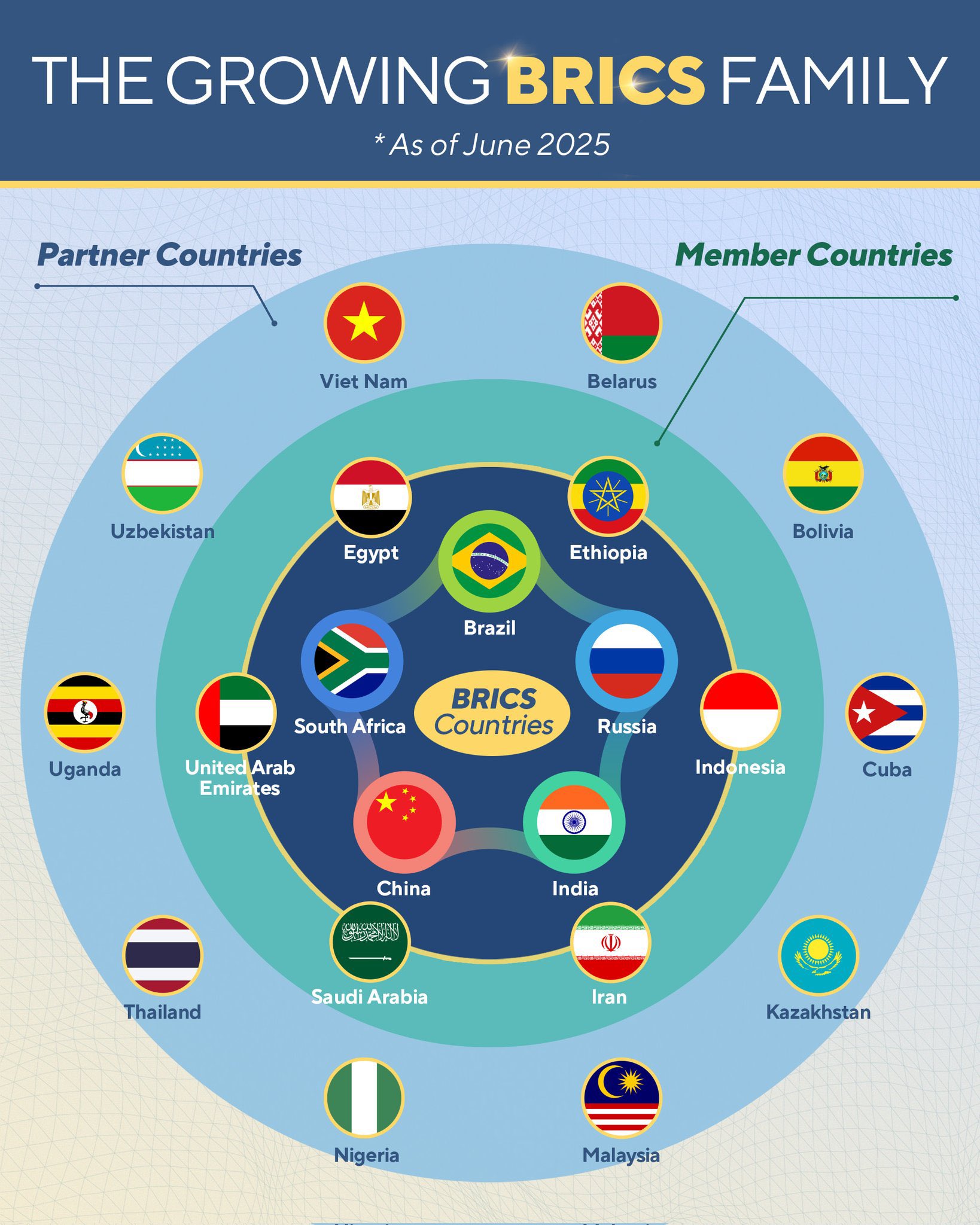
Context:
Vietnam has officially joined the BRICS group as a “Partner Country,” marking a milestone in its growing diplomatic and economic engagement on the global stage. This category was introduced during the 2024 BRICS Summit held in Kazan, Russia, as part of the bloc’s efforts to expand global engagement without immediate full membership.
Partner Country Status:
Vietnam is now the 10th country to be officially recognized under this category. The current list of BRICS partner countries includes:
- Vietnam
- Belarus
- Bolivia
- Kazakhstan
- Cuba
- Malaysia
- Nigeria
- Thailand
- Uganda
- Uzbekistan
This model allows BRICS to collaborate with a wider set of countries on shared goals such as economic development, South-South cooperation, financial reform, and multipolar diplomacy—without requiring full integration into the decision-making framework.
Economic and Strategic Benefits for Vietnam:
- Market Access: Closer ties with BRICS economies could open new trade and investment avenues.
- Development Cooperation: Vietnam can tap into development finance through institutions like the New Development Bank (NDB).
- Technology & Infrastructure: Opportunities in digital infrastructure, renewable energy, and transportation.
- Diplomatic Leverage: Greater visibility and voice in reshaping global institutions.
About BRICS:
BRICS is an acronym that stands for Brazil, Russia, India, China, and South Africa. The term BRIC (Brazil, Russia, India, and China) was coined by British economist Jim O'Neill in 2001. This grouping represents some of the world's largest emerging economies, which have significant influence in global affairs.
Formation: BRIC started functioning as a formal grouping in 2006, with its first summit held in Russia in 2009.
-South Africa joined the grouping in 2010, making it BRICS.
Members:
· Initial 5 members: Brazil, Russia, India, China, and South Africa.
· New members (BRICS+): Egypt, Ethiopia, Iran, Indonesi, and the United Arab Emirates.
Significance:
· Population: BRICS countries represent 45% of the world's population.
· GDP: The bloc accounts for 37.3% of world GDP, surpassing the EU's 14.5% and the G7's 29.3%.
Objectives:
· Promoting Cooperation: BRICS aims to foster cooperation among its member countries in areas such as economics, politics, and social development.
· Challenging Global Governance: The bloc seeks to challenge the existing global governance structures and promote a more multipolar world order.
Conclusion:
Vietnam’s accession as a BRICS partner country represents a strategic alignment of mutual interests. For BRICS, it adds economic diversity and geopolitical depth. For Vietnam, it offers new avenues to strengthen its role as a rising global player. As global dynamics shift toward multipolarity, Vietnam’s balanced approach and active multilateralism could serve as a model for others navigating an increasingly complex world order.