Context:
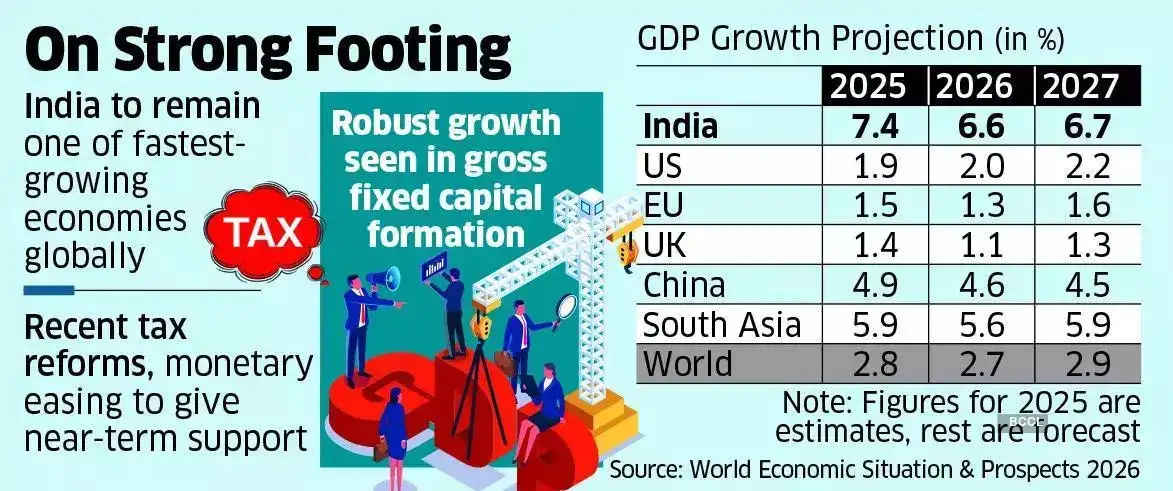
A day after the Union government projected India’s economy to grow at 7.4% in FY 2025–26, the United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs (UN DESA), in its World Economic Situation and Prospects 2026 (WESP 2026) report, pegged India’s growth at 7.2% for the current fiscal year. The assessment highlights India’s economic resilience amid rising global trade uncertainties, particularly those stemming from higher U.S. tariffs.
Key Drivers of India’s Growth:
1. Resilient Domestic Demand
Private consumption continues to remain robust, supported by rising incomes, stable employment conditions, and strong performance of the services sector.
2. Public Investment Push
The report underlines strong growth in gross fixed capital formation in 2025, driven by increased government expenditure on:
-
-
-
-
- Physical and digital infrastructure
- Defence
- Renewable energy
- Physical and digital infrastructure
-
-
-
3. Policy Support Measures
-
-
-
-
- Tax reforms, and
- Monetary easing
- Tax reforms, and
-
-
-
are expected to provide additional near-term stimulus to demand and investment.
External Risks and Mitigating Factors:
-
-
-
- Impact of U.S. Tariffs: Nearly 18% of India’s exports are directed to the United States, making tariff measures a potential downside risk to growth.
- Export Market Diversification: Strong demand from Europe and West Asia is expected to cushion India against prolonged global trade disruptions.
- Sectoral Outlook: On the supply side, manufacturing and services are expected to remain the primary engines of growth throughout the forecast period, reinforcing India’s medium-term economic prospects.
- Impact of U.S. Tariffs: Nearly 18% of India’s exports are directed to the United States, making tariff measures a potential downside risk to growth.
-
-
Global Comparison:
-
-
-
- While India is expanding its investment cycle, China has witnessed a contraction in fixed asset investment during the first three quarters of 2025 due to persistent weakness in its property sector.
- In contrast, Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) countries continue large-scale capital investments aligned with long-term economic diversification strategies.
- Growth in the United States and the European Union remains moderate, with fiscal and monetary measures helping cushion headwinds from external shocks such as tariffs.
- While India is expanding its investment cycle, China has witnessed a contraction in fixed asset investment during the first three quarters of 2025 due to persistent weakness in its property sector.
-
-
About UN DESA:
The United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs (UN DESA) is a core component of the UN Secretariat, responsible for advancing the development pillar of the United Nations. Headquartered at the UN Headquarters in New York, it serves as the institutional home of the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) and acts as a vital interface between global policy frameworks and national implementation.
Established:
-
-
- Founded in 1948
- Restructured into its present form in 1997 to strengthen coordination on sustainable development
- Founded in 1948
-
Key Functions:
UN DESA’s work spans three broad areas:
1. Analysis and Thought Leadership
-
-
-
-
- Functions as the UN’s economic and social think tank
- Produces data, projections, and policy options for Member States
- Functions as the UN’s economic and social think tank
-
-
-
2. Intergovernmental Support
-
-
-
-
- Provides secretariat support to:
- UN General Assembly
- Economic and Social Council (ECOSOC)
- High-Level Political Forum (HLPF)
- UN General Assembly
- Provides secretariat support to:
-
-
-
3. Capacity Building
-
-
-
-
- Offers technical assistance to help countries implement the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development
- Offers technical assistance to help countries implement the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development
-
-
-
Conclusion:
The UN DESA assessment reflects strong confidence in India’s growth fundamentals, driven by resilient domestic demand, sustained public investment, and policy support measures, even as global trade tensions persist. The outlook reinforces India’s position as a key driver of global economic growth in an otherwise slowing world economy.