Context:
India launched its first-of-its-kind R&D Roadmap for CCUS on 2 December 2025. prepared by the Department of Science and Technology (DST) and inaugurated by Prof. Ajay Kumar Sood, Principal Scientific Adviser to the Government of India.
-
- It aims to guide coordinated action, foster collaboration, and accelerate deployment of CCUS technologies.
- Supports India’s goal of achieving net-zero emissions by 2070 and aligns with the vision of Viksit Bharat@2047.
- It aims to guide coordinated action, foster collaboration, and accelerate deployment of CCUS technologies.
Strategic Significance and Objectives:
-
- Climate Mitigation: Reduces India’s carbon footprint, particularly in hard-to-abate sectors such as power, cement, and steel.
- Technology Advancement: Balances the commercial readiness of current technologies with next-generation, breakthrough scientific solutions.
- Global Leadership: Reinforces India’s position as a responsible global partner in climate action.
- Sustainable Development: Integrates industrial growth with environmental responsibility.
- Climate Mitigation: Reduces India’s carbon footprint, particularly in hard-to-abate sectors such as power, cement, and steel.
Implementation Framework
-
- Translational R&D: DST has established CCUS test beds in industrial environments to validate technologies.
- Public-Private Partnerships (PPPs): Encourages innovative collaborations for faster deployment.
- National Excellence Centres: DST has set up three National Centers of Excellence in CCUS.
- Supportive Frameworks: Emphasizes skilled human capital, regulatory and safety standards, and shared infrastructure.
- Funding and Strategic Guidance: Linked with initiatives like the ₹1 Lakh Crore Research, Development & Innovation (RDI) Scheme, promoting private-sector-led innovation.
- Translational R&D: DST has established CCUS test beds in industrial environments to validate technologies.
About India’s Commitment to Net Zero Emissions target:
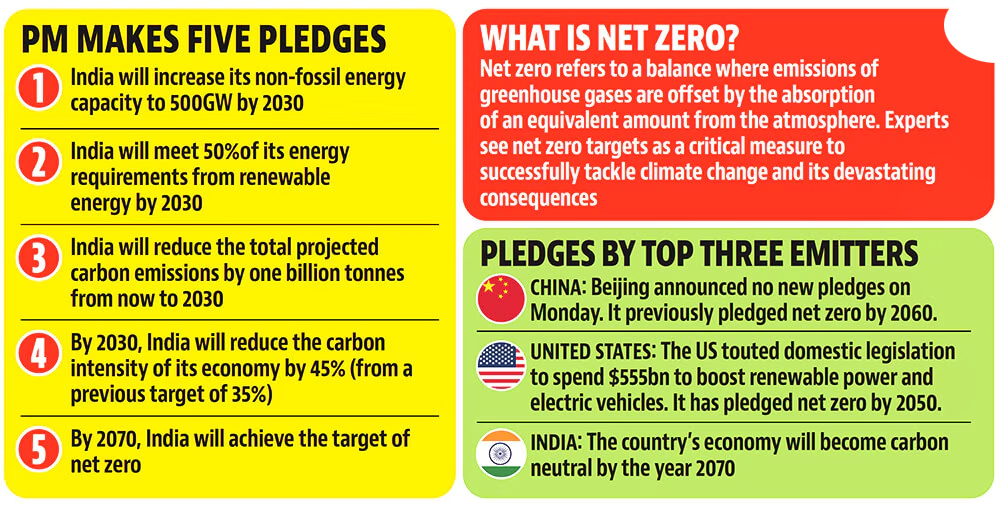
· India is committed to achieving net-zero greenhouse gas emissions by 2070.
· This commitment aligns with the broader Panchamrit declaration made at COP26 (Glasgow, 2021).
About short- and long-term climate targets:
-
- Non-fossil fuel energy capacity of 500 GW by 2030.
- Renewable energy to meet at least 50% of total energy requirements by 2030.
- CO₂ emissions reduction by 1 billion tons by 2030.
- Carbon intensity reduction to below 45% by 2030.
- These targets lay the foundation for achieving net-zero emissions by 2070.
- Non-fossil fuel energy capacity of 500 GW by 2030.
Strategies that India adopted:
-
- Shift to clean energy alternatives including solar, wind, and hydropower.
- Hydrogen energy initiatives, including the National Hydrogen Energy Mission and production-linked incentives.
- Enhanced manufacturing capacities for renewable energy and energy efficiency.
- Emerging technologies: 2G ethanol pilot, hydrogen valleys, comfort climate box for tropical regions, heating and cooling virtual repository.
- Bio-based economy: Roadmap toward $150 billion by 2025, supporting advanced biofuels and waste-to-energy technologies.
- Shift to clean energy alternatives including solar, wind, and hydropower.
Conclusion
The CCUS R&D Roadmap is a strategic instrument for India’s climate action, providing guidance on technology development, funding, and collaboration. It positions India to meet its net-zero commitments by 2070, strengthen its sustainable development agenda, and enhance global climate leadership.






