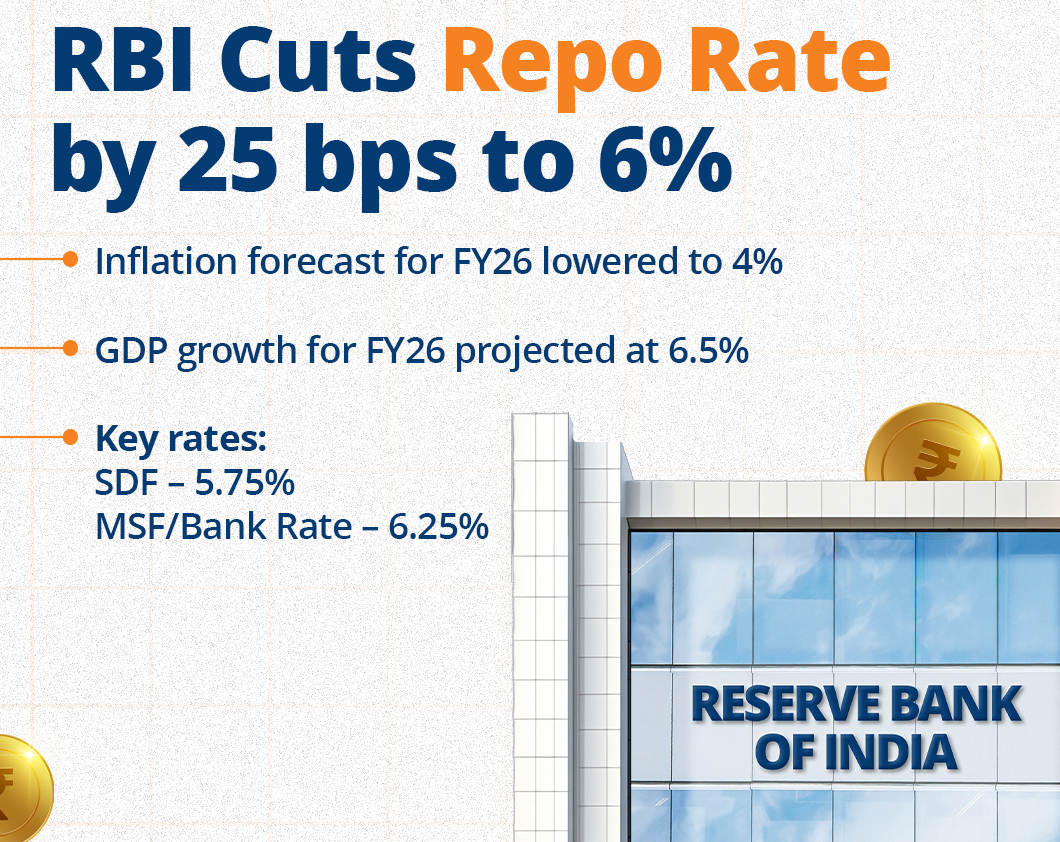
Context:
On April 9, 2025, the Reserve Bank of India’s (RBI) six-member Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) announced a reduction in the repo rate by 25 basis points, bringing it down to 6%. Along with this, the RBI changed its monetary policy stance from “neutral” to “accommodative”, indicating the possibility of further rate cuts in the future. This decision comes at a time of global economic uncertainty and domestic growth concerns.
About the Repo Rate:
- The repo rate is the interest rate at which commercial banks take loans from the RBI. It helps decide the overall interest rates in the economy. The reverse repo rate is the interest rate the RBI pays to banks when they deposit extra money with it.
- Currently, the repo rate is 6%, and the reverse repo rate is 3.35%.
- When the RBI lowers the repo rate, banks can borrow money at a lower cost. This allows them to reduce loan interest rates, making borrowing cheaper for businesses and individuals.
- On the other hand, when the RBI increases the repo rate, loans become more expensive. This reduces borrowing and helps control inflation.
Reason behind reducing the Repo Rate:
The RBI’s decision to cut the repo rate is influenced by both global and domestic economic factors.
1. Global Uncertainty: The trade tensions created by the reciprocal tariffs imposed by the United States under the Trump administration have led to instability in global markets. RBI Governor Sanjay Malhotra noted that reviving economic growth is a bigger concern than inflation at this point.
2. Controlled Inflation: The average inflation rate in January-February 2025 was 3.9%, which is lower than the RBI’s projection of 4.8% for the fourth quarter of FY 2025. Since inflation remains within manageable levels, the RBI has more flexibility to support economic growth by reducing interest rates.
Impact of the Rate Cut
1. Boosting Economic Growth: Lower borrowing costs make loans cheaper for businesses and individuals, encouraging investment, spending, and job creation.
2. Potential Inflationary Pressure: While lower interest rates help growth, they can also increase money supply, which might lead to higher inflation in the future.
3. Changes in Banking Sector Rates: Commercial banks may reduce their lending rates, making home, vehicle, and business loans more affordable, but also lowering interest rates on deposits.
4. Future Monetary Policy: The RBI’s accommodative stance suggests that if economic conditions do not improve, further repo rate reductions may follow to stimulate growth.
Conclusion
The RBI’s repo rate cut reflects its strategy to support economic growth amid global challenges. By making borrowing cheaper, the central bank aims to encourage investment and spending. However, closely monitoring inflation and external economic conditions will be essential to maintain a balanced monetary policy.