Context:
India’s state-owned Bharat Electronics Limited (BEL) and French firm Safran Electronics and Defence (SED) recently signed a joint venture cooperation agreement (JVCA) for the production of Highly Agile Modular Munition Extended Range (HAMMER) smart precision Guided air-to-ground weapons in India.
Key Features of the HAMMER System:
-
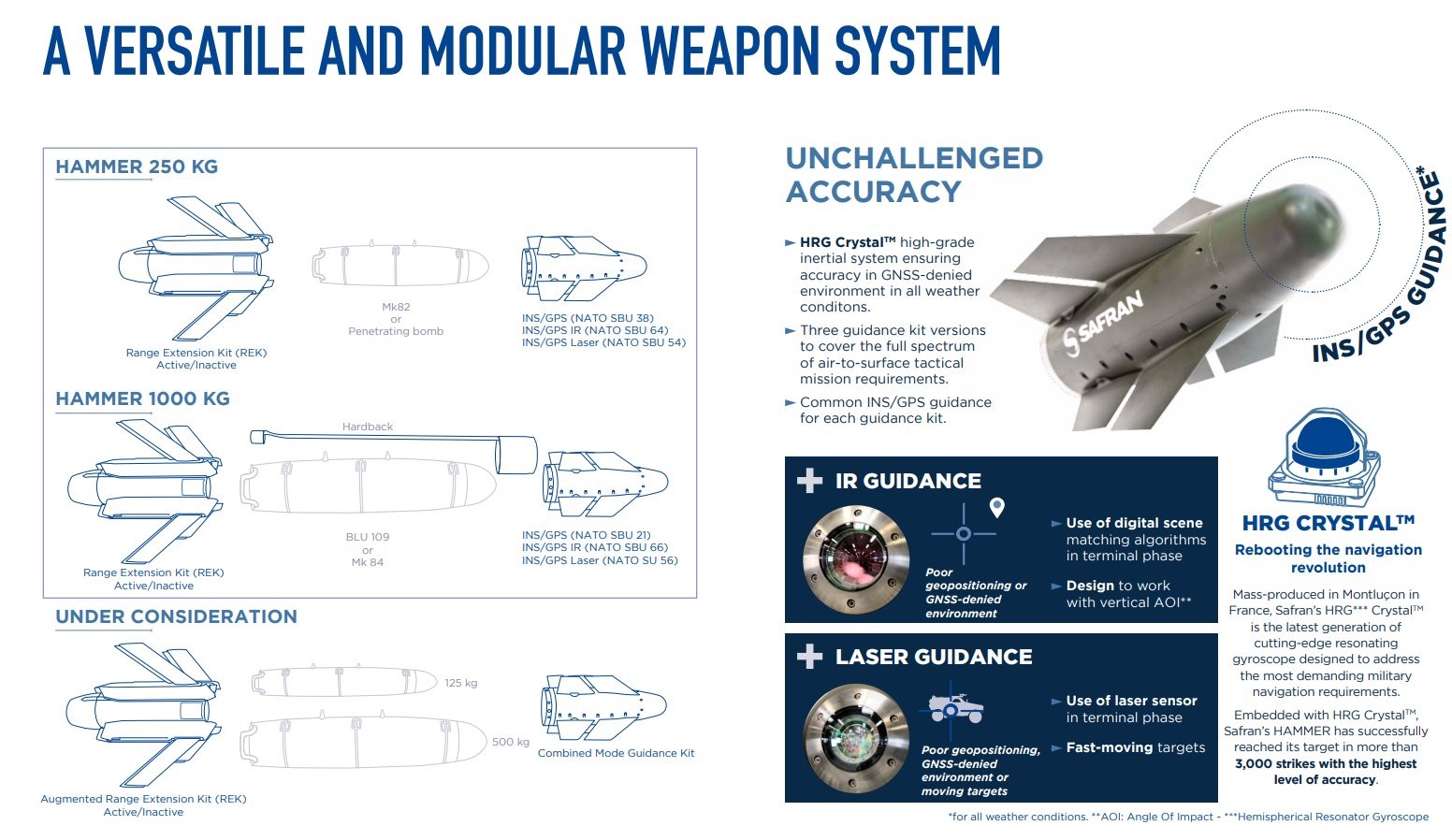
- The HAMMER munition is modular, meaning its design allows different warhead sizes (250 kg, 500 kg, 1000 kg) to be used.
- It has a range of up to ~70 km, giving it long-standoff capability.
- It’s all-weather and resilient: the weapon is “insensitive to jamming” and can be launched from low altitudes and rough terrain.
- Highly accurate and combat-proven; it supports different guidance systems (e.g., GPS/INS, infrared).
- Compatible with several platforms, such as France’s Rafale jets and India’s Tejas aircraft.
- The HAMMER munition is modular, meaning its design allows different warhead sizes (250 kg, 500 kg, 1000 kg) to be used.
Structure and Aims of the Joint Venture:
-
- The agreement establishes a 50:50 joint venture (JV) between BEL and Safran.
- The JV will not just manufacture HAMMER, but also handle customisation, supply, and maintenance.
- Phase-wise localisation: Indigenisation will gradually rise to ~60%, focusing on electronics, subassemblies, mechanical parts.
- BEL will lead the final assembly, testing, and quality assurance.
- The agreement establishes a 50:50 joint venture (JV) between BEL and Safran.
Implications for India’s Defence Posture:
-
- The JV is emblematic of India’s strategic shift: from being a large importer of arms to being a hub for manufacturing and possibly exporting advanced weapons.
- It also underlines a diversified defence procurement strategy: not relying solely on Russia, USA, or others, but deepening partnerships with European players like France.
- For India’s air power, the domestic production of HAMMER can significantly boost the strike capabilities of platforms like the Rafale and Tejas, making them more potent in a future high-intensity conflict.
- The JV is emblematic of India’s strategic shift: from being a large importer of arms to being a hub for manufacturing and possibly exporting advanced weapons.
About India and France defence relations:
-
-
- India and France share a strong defence partnership, covering military hardware, technology transfer, joint exercises, and strategic cooperation.
- India is acquiring 26 Rafale-M naval fighters from France, including tech transfer and local production facilities.
- Industrial collaboration exists in submarine construction: the P-75 Scorpene project, with French tech transfer to Mazagon Dockyard.
- India and France share a strong defence partnership, covering military hardware, technology transfer, joint exercises, and strategic cooperation.
-
Major joint military exercises:
· Varuna — navy exercise between Indian and French navies.
· Shakti — army-level exercise.
· Garuda — air-force exercise between IAF and French Air & Space Force.
Conclusion:
The India–France JV to manufacture HAMMER air-to-ground weapons is a major step toward defence self-reliance. It boosts India’s industrial capacity, enhances precision-strike capability, and strengthens bilateral ties by shifting the partnership from buyer–seller to co-producer. Its success, however, will depend on effective technology transfer, high localisation, and scalable production.