Context:
A landmark study published in Science (June 2025) by researchers from the US National Institutes of Health, Capstan Therapeutics, and the University of Pennsylvania has introduced a novel method to engineer CAR T-cells entirely inside the human body. The technique uses messenger RNA (mRNA) and lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) to directly instruct immune cells to target and destroy disease-causing cells — without lab-based modification, chemotherapy, or hospital-intensive procedures.
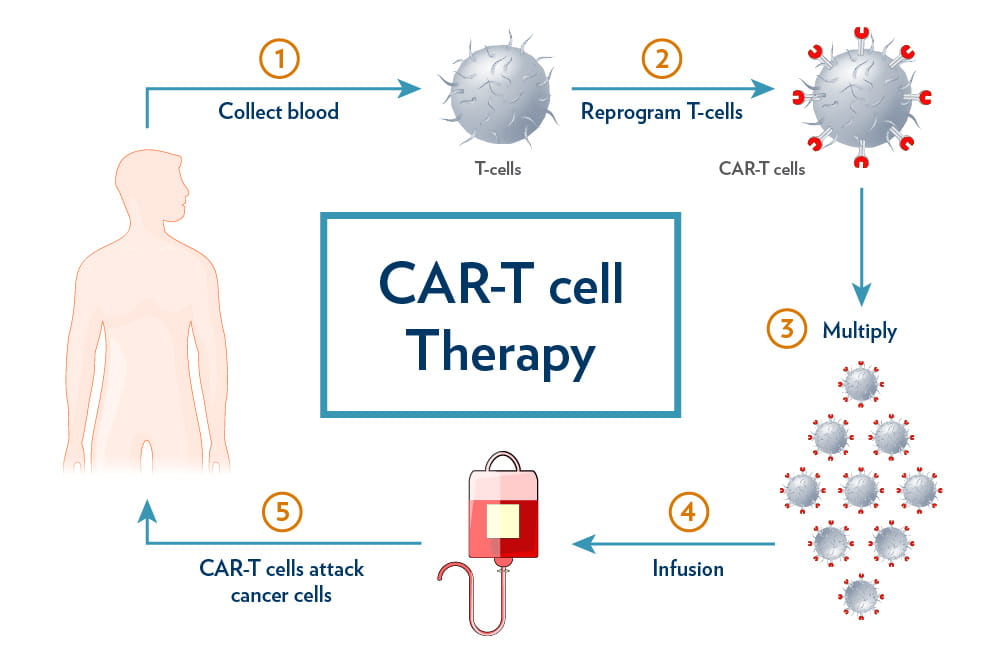
About CAR T-Cell Therapy:
Chimeric Antigen Receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy is a form of immunotherapy where a patient’s T cells are extracted, genetically engineered to detect cancer-specific markers (commonly CD19 on B cells), and reinfused to destroy the malignant cells.
· It has been used effectively in aggressive blood cancers such as diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and acute lymphoblastic leukaemia, offering long-term remissions for patients who fail standard treatments.
· However, the therapy is costly, slow, and infrastructure intensive. In India, the estimated cost is ₹60–70 lakh per patient, with about half spent on lab-based cell modification and the rest on hospitalisation, chemotherapy, and management of side effects like infections.
Engineering T-Cells Inside the Body:
The new study bypasses conventional steps by using CD8-targeted lipid nanoparticles (CD8-tLNPs) to deliver mRNA directly to circulating immune cells. These nanoparticles are equipped with antibodies that home in on CD8+ T cells, instructing them to express synthetic receptors — such as those targeting CD19 or CD20 — and convert into cancer-fighting cells inside the body.
- In mice, this led to tumour regression and widespread B-cell depletion.
- In monkeys, after 2–3 infusions, up to 85% of CD8+ T cells were reprogrammed, eliminating 95% of B cells across tissues like spleen, bone marrow, and lymph nodes.
Key Advantages of the Study:
- No personalised cell manufacturing: Removes need for complex lab-based processing.
- No chemotherapy needed: Avoids lymphodepleting regimens, reducing infection risk.
- mRNA-based: Temporary cell modification lowers long-term genetic risks.
- Simplified delivery: Acts like a drug infusion, reducing dependence on specialised centres.
- Improved safety profile: A new biodegradable lipid (Lipid 829) reduced liver toxicity and inflammation.
The approach was also tested in blood samples from lupus and myositis patients, successfully eliminating faulty B cells — suggesting potential in treating autoimmune disorders as well.
Relevance for India:
India bears a high burden of B cell-driven cancers:
- DLBCL accounts for 34–60% of non-Hodgkin lymphoma cases.
- Acute lymphoblastic leukaemia is the most common childhood cancer.
Autoimmune diseases are rising, with an estimated 30% increase in prevalence post-COVID-19.
Current CAR T-cell therapy in India remains limited by high cost, infrastructure requirements, and limited access to specialised centres.
This new infusion-based method could significantly reduce costs and increase reach — making it especially valuable in public hospitals and tier-2 or tier-3 cities.
Conclusion:
While the platform is still in preclinical stages, its ability to engineer T cells inside the body, without the need for chemotherapy or personalised labs, represents a significant technological leap. If proven effective in human trials, it could expand the use of CAR T-cell therapy to more patients, including the elderly and those with comorbidities — and reshape the future of cancer and autoimmune treatment in India and beyond.