Context:
On July 24, 2025, the Union Sports Minister Mansukh Mandaviya introduced the National Sports Governance Bill in the Lok Sabha. The Bill seeks to reform the structure and regulation of sports governance in India, bringing bodies like the BCCI under a statutory framework, and introducing mechanisms to ensure greater transparency, accountability, and speedy dispute resolution.
Significance of the Bill:
It is found that, existing regulatory framework in Indian sports was based on executive guidelines like the National Sports Code (2011), which lacked statutory authority.
Several National Sports Federations (NSFs) have faced issues of:
- Poor governance
- Lack of transparency
- Electoral malpractices
- Judicial interventions due to internal disputes
There was no single institutional mechanism for oversight, leading to fragmented and inconsistent regulation.
India’s aspirations to become a global sports power required a more structured, independent, and robust governance framework.
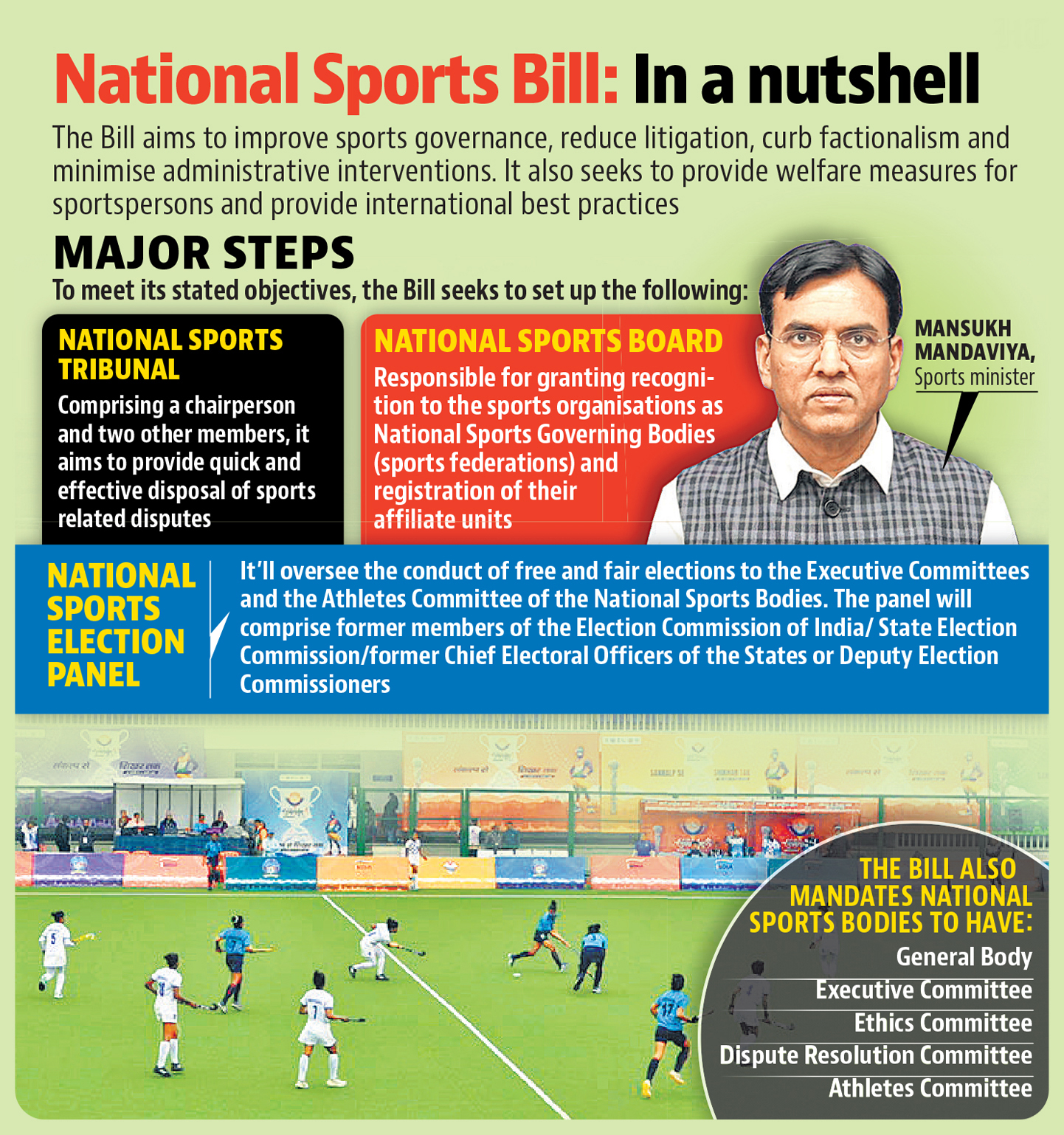
Key Features of the National Sports Governance Bill
1. Formation of a National Sports Board
- A statutory, autonomous body with powers to:
- Regulate, recognize, and oversee all National Sports Federations (including BCCI)
- Ensure adherence to governance standards
- Register affiliated state/district units
- Monitor financial and operational performance
2. Creation of a National Sports Tribunal
- A quasi-judicial body with powers equivalent to a civil court
- Handles disputes related to:
- Athlete selection
- Federation elections
- Internal governance of sports bodies
- Its decisions are binding and can be challenged only in the Supreme Court
- Aims to reduce dependency on regular courts and expedite decisions
3. Uniform Registration and Data Transparency
- All sports bodies must be registered with the Board.
- The Bill mandates creation of a central database of federations and affiliates.
- Facilitates public access and accountability.
4. Changes in Tenure and Age Caps
- Increases upper age limit for sports administrators to 75 years
- Removes term limits, to allow longer tenures in federations
Strengths of the Bill
· Institutional clarity: Replaces fragmented governance with a unified National Sports BoardEfficient redressal: Tribunal avoids delays of regular courts
· Transparency: Central registry improves public access to information
· Global alignment: Brings India in sync with international sports governance frameworks
Challenges and Criticisms
· Tribunal independence: Must avoid political or bureaucratic interference
· Age & tenure limits: Risk of entrenched leadership; may weaken fresh leadership opportunities
· BCCI integration: Resistance likely from a powerful and autonomous body
· Athlete access: Tribunal must remain financially and legally accessible to underprivileged athletes
Conclusion:
The National Sports Governance Bill, 2025 is a welcome legislative step towards reforming India’s fragmented and often opaque sports administration ecosystem. By establishing a National Sports Board and Tribunal, it aims to institutionalize transparency, efficiency, and accountability. However, its success will depend on ensuring true independence, maintaining athlete rights, and avoiding administrative overreach.






