Context:
The Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY) has recently approved 22 additional proposals under the Electronics Components Manufacturing Scheme (ECMS), a key pillar of the government’s strategy to strengthen domestic electronics manufacturing and reduce dependence on imports.
About the Electronics Components Manufacturing Scheme (ECMS):
-
-
- The Electronics Components Manufacturing Scheme (ECMS) is a flagship initiative of the Government of India, launched in April 2025 by MeitY.
- ECMS is a production-linked incentive (PLI)-style scheme designed to encourage the domestic manufacture of electronic components and parts.
- The scheme aims to boost local value addition, attract investments, generate employment, and support emerging sectors such as mobile phones, telecommunications, consumer electronics, automotive electronics, IT hardware, and strategic electronics.
- It builds on earlier policy efforts to deepen India’s electronics manufacturing ecosystem, complementing existing PLI schemes for smartphones and other electronic hardware.
- The Electronics Components Manufacturing Scheme (ECMS) is a flagship initiative of the Government of India, launched in April 2025 by MeitY.
-
Key Features of the Latest Approvals:
-
-
- Investment and Production
- The 22 newly approved projects involve a projected investment of approximately ₹41,863 crore.
- They are expected to generate production valued at around ₹2,58,152 crore.
- The 22 newly approved projects involve a projected investment of approximately ₹41,863 crore.
- Employment Generation
- These projects are likely to create nearly 33,791 direct jobs.
- Additional indirect employment is expected across ancillary and supporting industries.
- These projects are likely to create nearly 33,791 direct jobs.
- Product Coverage
- The approvals span 11 key product segments, including critical components such as printed circuit boards (PCBs), capacitors, connectors, enclosures, and lithium-ion cells.
- They also include sub-assemblies such as camera and display modules, as well as essential supply-chain inputs like aluminium extrusions and anode materials.
- The approvals span 11 key product segments, including critical components such as printed circuit boards (PCBs), capacitors, connectors, enclosures, and lithium-ion cells.
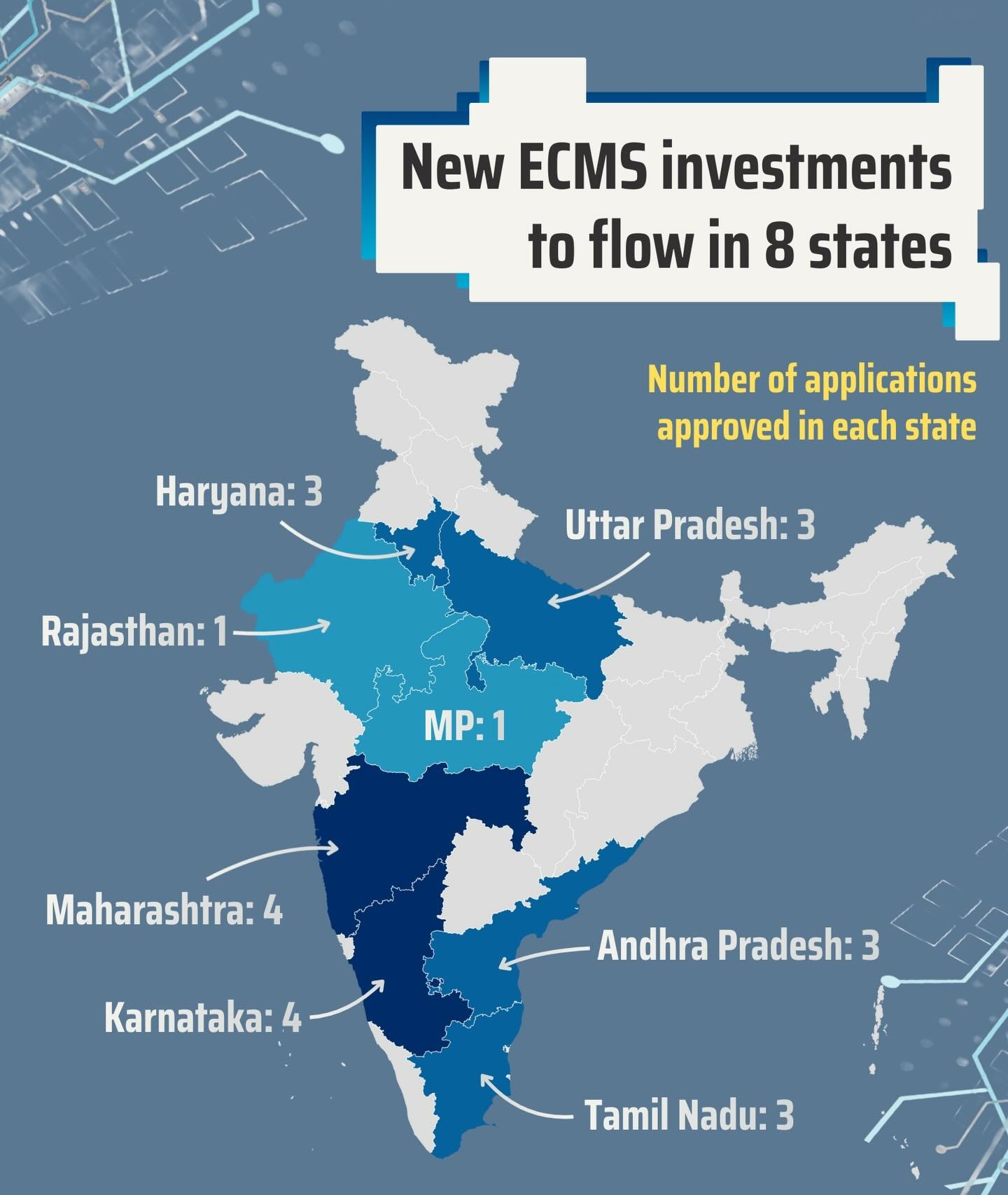
- Geographical Spread
- Manufacturing facilities will be established across multiple states, including Andhra Pradesh, Haryana, Karnataka, Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra, Tamil Nadu, Uttar Pradesh, and Rajasthan.
- This reflects a deliberate strategy to promote geographically balanced industrial development.
- Manufacturing facilities will be established across multiple states, including Andhra Pradesh, Haryana, Karnataka, Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra, Tamil Nadu, Uttar Pradesh, and Rajasthan.
- Investment and Production
-
Significance:
-
-
- Strengthening Domestic Supply Chains: By encouraging local manufacturing of electronic components, the scheme addresses a major structural weakness in India’s electronics sector—its heavy reliance on imported parts and sub-components.
- Employment and Investment Boost: The scale of projected investment and job creation highlights the government’s focus on expanding industrial capacity and fostering high-skill employment in electronics manufacturing.
- Value Chain Development: Supporting production across a wide range of components and sub-assemblies helps build end-to-end domestic value chains, reducing supply vulnerabilities and enhancing global competitiveness.
- Strengthening Domestic Supply Chains: By encouraging local manufacturing of electronic components, the scheme addresses a major structural weakness in India’s electronics sector—its heavy reliance on imported parts and sub-components.
-
Conclusion:
The approval of 22 additional projects under the Electronics Components Manufacturing Scheme reflects a sustained policy thrust to position India as a global hub for electronics manufacturing. By attracting substantial investments, generating employment, and promoting domestic production of critical components, the initiative seeks to make India’s electronics ecosystem more self-reliant, resilient, and competitive in an increasingly technology-driven global economy.