Context:
The Indian government has launched a nationwide crackdown on alleged illegal Bangladeshi immigrants, which has resulted in over 2,000 individuals being pushed back across the border since May 7.
· National Security Threats: Illegal immigrants are often linked to terrorism, human trafficking, and hawala networks, posing a significant threat to national security. There have been cases of Bangladeshi nationals involved in terror training and radicalization, fake currency distribution, and drug trafficking.
· Demographic Changes: The influx of illegal immigrants is altering the demographic landscape in states like West Bengal and Delhi, potentially leading to social unrest and communal tensions.
· Economic Burden: Illegal immigrants may strain local resources, access government welfare schemes, and impact the labor market, potentially leading to economic instability.
Potential implications:
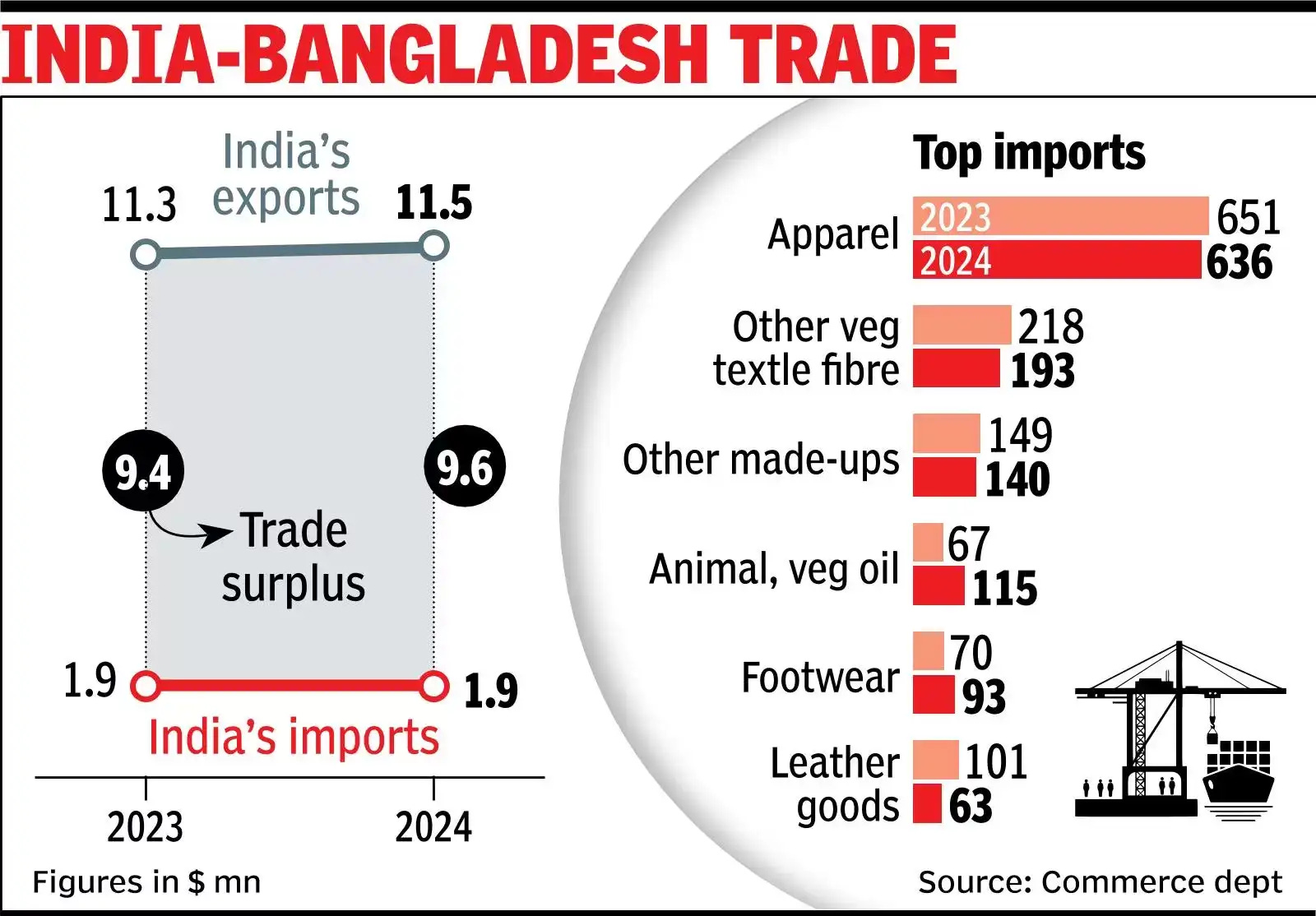
· The crackdown may strain diplomatic relations between India and Bangladesh, potentially affecting trade and economic cooperation.
· The issue may have implications for regional stability, particularly in the context of South Asian geopolitics.
· The crackdown may attract international attention, particularly from human rights organizations, which may criticize India's handling of the issue.
Who are Illegal migrants or immigrants?
According to the Citizenship Act, 1955, an illegal migrant in India is defined as:
· Foreigner entering without valid documents: A person who enters India without a valid passport or other prescribed travel documents.
· Overstaying: A person who enters India with a valid passport or other prescribed travel documents but remains in India beyond the permitted time period.
Causes of Illegal Immigration:
· Socio-economic Factors: Poverty, lack of opportunities, and socio-economic instability in source countries drive individuals to seek better lives elsewhere.
· Political Instability and Conflict: Religious persecution, political violence, and conflicts lead to displacement and migration.
· Environmental Factors: Climate change, natural disasters, and resource scarcity contribute to forced migration.
Strategies to Address Illegal Immigration:
· Strengthening border infrastructure with fences, border roads, and floodlighting, and establishing more border outposts.
· Utilizing technology like the Comprehensive Integrated Border Management System (CIBMS) and deploying additional manpower, special surveillance equipment, and force multipliers in vulnerable areas.
· Negotiating bilateral agreements with origin countries to address illegal migration, establish legal migration pathways, and facilitate returns of deported individuals.
· Developing comprehensive immigration policies that address the needs of refugees, asylum seekers, and legal migrants, while also addressing concerns about security and border control.
Conclusion:
India’s crackdown on illegal Bangladeshi immigrants reflects growing concerns over national security, demographic shifts, and economic pressures. While the government’s efforts aim to uphold internal security and legal order, the issue demands a balanced approach that safeguards human rights, sustains diplomatic ties with Bangladesh, and develops long-term regional cooperation on migration management.