Context:
The World Economic Forum’s Global Gender Gap Report 2025 was launched recently.
India’s Overall Ranking and Score:
India has slipped two positions from last year, ranking 131 out of 148 countries. It had ranked 129 in 2024.
India’s overall gender parity score is 64.1%, placing it among the lowest-ranked countries in South Asia.
Dimension-Wise Performance:
1. Economic Participation and Opportunity
- India improved slightly in this area, with the score rising from 39.8% to 40.7%.
- The estimated earned income parity increased from 28.6% to 29.9%.
- Labour force participation remained unchanged at 45.9%, which is India’s highest so far.
2. Educational Attainment
- India scored 97.1% in this subindex.
- The rise is due to better female literacy rates and increased enrolment in higher education.
- This suggests that gender gaps in education are closing steadily.
3. Health and Survival
- India showed improved parity in this dimension.
- Gains were mainly due to better sex ratio at birth and healthy life expectancy.
- However, the report noted that overall life expectancy has declined slightly for both men and women.
4. Political Empowerment
- India saw a decline in this area.
- Female representation in Parliament dropped from 14.7% to 13.8%.
- Women in ministerial roles declined from 6.5% to 5.6%.
- This led to a 0.6-point drop in the political empowerment score compared to last year.
South Asia and Global Context:
- Bangladesh ranked highest in South Asia, moving up 75 places to 24th position.
- Other South Asian rankings:
- Bhutan – 119
- Nepal – 125
- Sri Lanka – 130
- Maldives – 138
- Pakistan – 148 (last)
Globally, Iceland retained the top rank for the 16th year, followed by Finland, Norway, the UK, and New Zealand.
Global Trends and Challenges:
- The global gender gap has closed to 68.8%, the best progress since the COVID-19 pandemic.
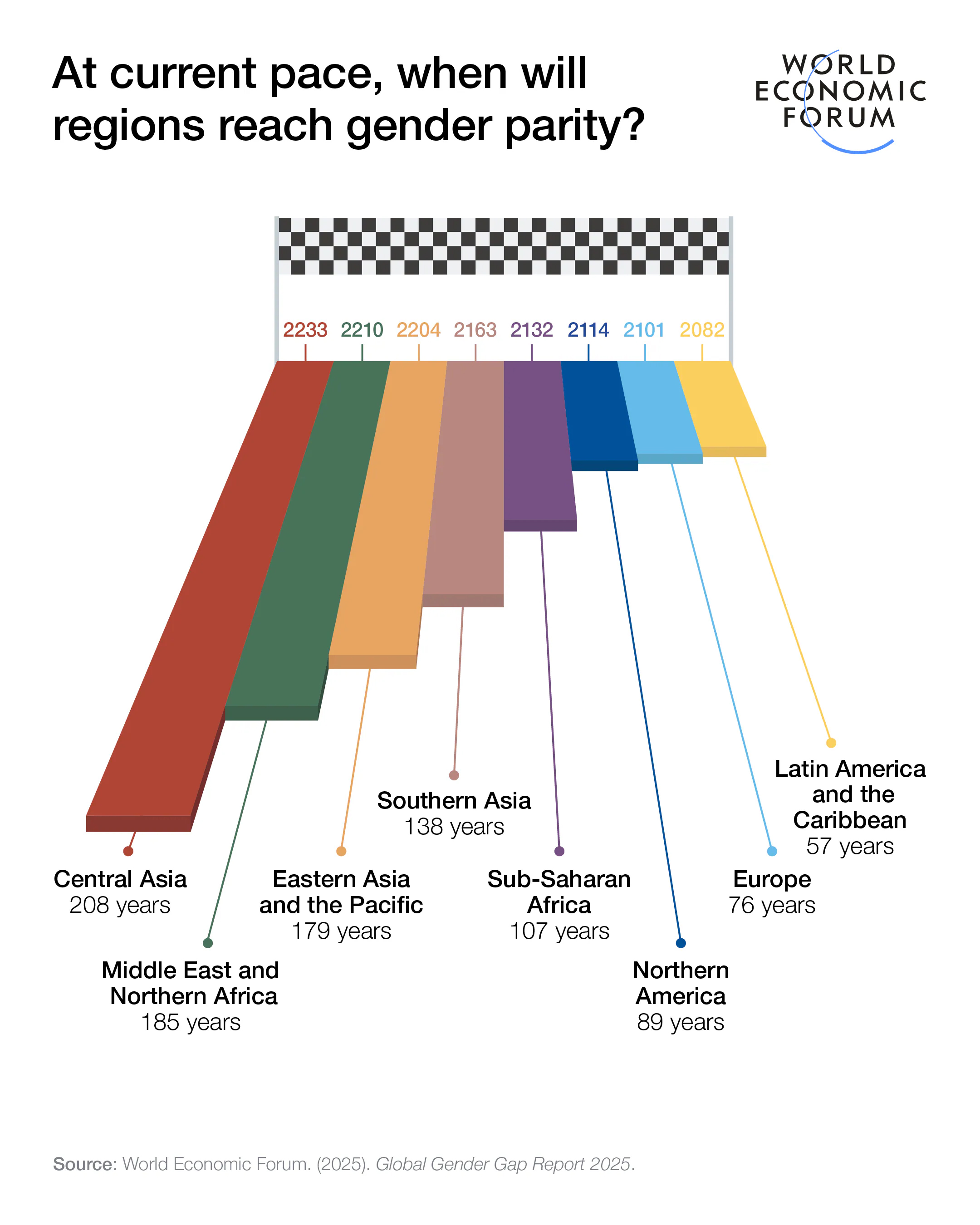
- At the current pace, full gender parity will take 123 years.
- Women now make up 41.2% of the global workforce, but only 28.8% of leadership positions.
About the Global Gender Gap Report 2025:
The Global Gender Gap Index is a yearly report first published in 2006 by the World Economic Forum. It is the world’s longest-running tool to measure gender equality.
It tracks progress in closing gender gaps across four main areas:
1. Economic Participation and Opportunity
2. Educational Attainment
3. Health and Survival
4. Political Empowerment
Score mechanism:
- Each area is scored between 0 and 1.
- A score of 1 means full equality, while 0 means complete inequality.
Significance of the Index:
- It helps countries compare their performance on gender equality.
- It acts as a guide to set goals and track improvements in areas like health, education, jobs, and politics.
- It helps policymakers and leaders focus on what matters most for their country’s context.
Conclusion:
As the world faces economic, technological, and demographic changes, gender parity is not just a social goal—it is also an economic necessity.