Context:
Recently, Global Carbon Budget (2025) released by the Global Carbon Project (GCP), found that India’s CO₂ emissions from fossil fuel sources in 2025 are projected to grow significantly lower than the 2024.
Key Findings of India specific:
· India’s fossil fuel-related CO₂ emissions are projected to increase by 1.4% in 2025, compared to 4% growth in 2024.
· Absolute emissions are expected to rise from 3.19 billion tonnes in 2024 to 3.22 billion tonnes in 2025.
· The growth rate is lower than that of the United States (1.9%), reflecting differences in energy demand and policy measures.
Key Drivers behind the India's Slower Growth:
1. Favourable Climate Conditions
-
-
- Early and widespread monsoon rains reduced:
- Electricity demand for air-conditioning
- Irrigation-related energy use
- Electricity demand for air-conditioning
- Early and widespread monsoon rains reduced:
-
2. Rapid Rise in Renewable Energy
-
-
- Strong capacity addition in solar and wind
- Higher renewable penetration in the electricity grid
- Lower marginal coal generation during peak periods
- Strong capacity addition in solar and wind
-
3. Moderation in Coal Consumption
-
-
- Coal is the largest contributor to India’s fossil emissions.
- Slower industrial demand and higher hydro generation during monsoon months also helped stabilise coal use.
- Coal is the largest contributor to India’s fossil emissions.
-
About the Global Findings:
-
- Record Fossil Fuel Emissions: Global fossil CO₂ emissions are projected to rise by 1.1% in 2025, reaching 38.1 billion tonnes. This increase is driven by all fuel types: coal (+0.8%), oil (+1%), and natural gas (+1.3%).
- Decoupling of Emissions and Economic Growth: Despite the overall increase, a significant positive is that 35 countries have successfully reduced their fossil carbon emissions over the past decade while their economies continued to grow.
- Varied Regional Trends:
- China is projected to see a 0.4% increase, a slower growth rate than in recent years due to a massive growth in renewable energy.
- India's emissions are projected to increase by 1.4%, also below recent trends.
- The USA (+1.9%) and the European Union (+0.4%) are projected to see slight increases in 2025, linked to factors like colder weather and lower renewable output in the EU.
- China is projected to see a 0.4% increase, a slower growth rate than in recent years due to a massive growth in renewable energy.
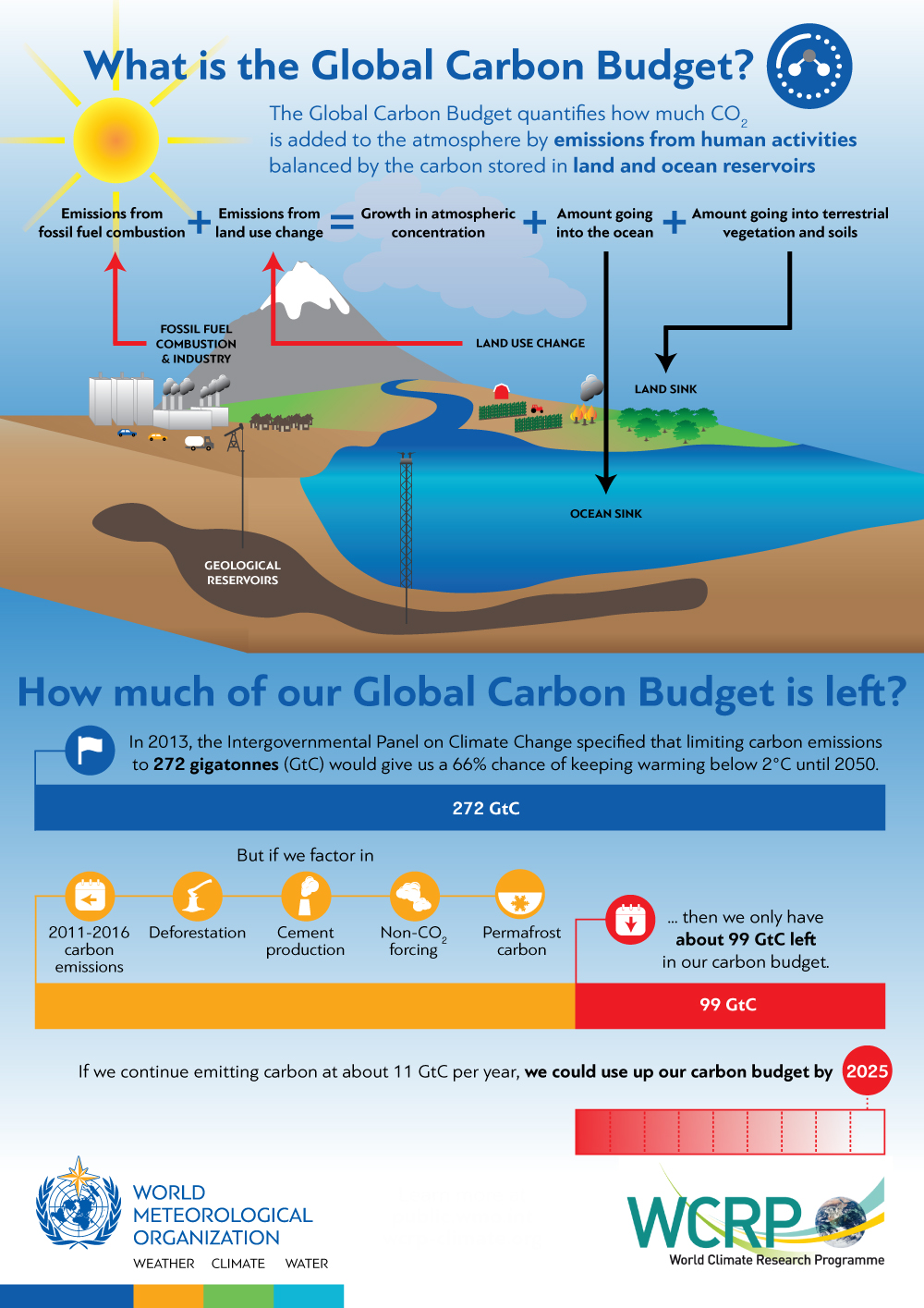
- Remaining Carbon Budget Nearly Exhausted: The remaining carbon budget to limit warming to 1.5°C is estimated at 170 billion tonnes of CO₂, which is equivalent to just four years of current emissions levels. At current rates, the world is not on track to meet the Paris Agreement goals.
- Record Fossil Fuel Emissions: Global fossil CO₂ emissions are projected to rise by 1.1% in 2025, reaching 38.1 billion tonnes. This increase is driven by all fuel types: coal (+0.8%), oil (+1%), and natural gas (+1.3%).
About Global Carbon Budget:
The Global Carbon Budget is an estimate of how much carbon dioxide (CO₂) humanity can emit while still keeping global warming below specific temperature thresholds, such as 1.5 °C above pre-industrial levels. Produced annually by the Global Carbon Project, this report tracks global CO₂ emissions from fossil fuels, land-use changes, and other sources, as well as the natural absorption of CO₂ by forests, soils, and oceans.