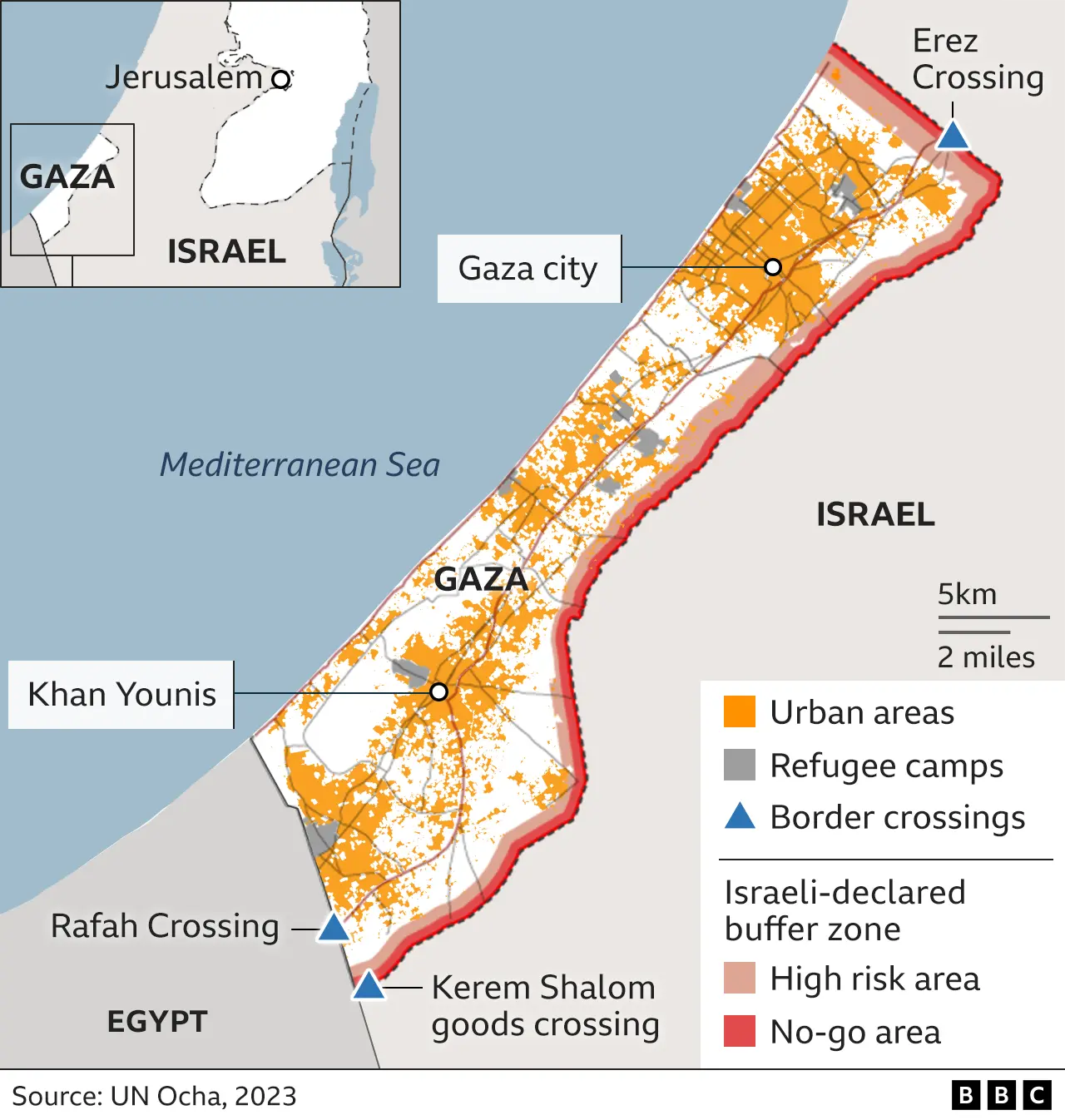
Context:
Recently, a historic ceasefire agreement was signed between Israel and Hamas in Sharm El-Sheikh, Egypt. The deal, brokered by the United States, Egypt, and Qatar, aims to end over two years of conflict and initiate a phased process of hostilities cessation, hostage exchanges, and reconstruction.
Key Provisions of the Deal:
1. Ceasefire / Pause in Hostilities
Fighting is to cease, allowing aid to flow into Gaza and reconstruction efforts to begin.
2. Hostage Release by Hamas
o All 20 living Israeli hostages held by Hamas are to be released.
o The release is to occur within 72 hours after the ceasefire takes effect.
3. Prisoner Exchange
o Israel will release Palestinian prisoners and detainees, numbering in the hundreds or possibly in the low thousands, including those held during the conflict.
o Some of these will include long‑term prisoners.
4. Israeli Military Pullback & Humanitarian Access
o Israel will partially withdraw troops from Gaza zones. Aid — food, medical, fuel — will be allowed unhindered into Gaza to address the severe humanitarian crisis.
o Reconstruction, clearing of rubble, restoring infrastructure will be among major tasks.
5. Guarantees & Oversight
o Mediators (U.S., Qatar, Egypt, Turkey) have promised to provide guarantees on implementation and monitor compliance.
o Hamas’ Gaza leadership has stated it accepted guarantees from the United States and other mediators confirming the war's end.
Challenges & Risks Ahead:
-
- Implementation: Ceasefire deals often falter. Ensuring both sides adhere to the agreement is a major challenge.
- Trust deficit: Years of conflict have eroded trust. People may doubt each side’s willingness to stick to the terms.
- Transition governance: Who will run Gaza? The role of Hamas, the Palestinian Authority, international oversight — all are contentious.
- Resurgence of violence: If any violation occurs or agreement halves, fighting could resume.
- Reconstruction & justice: Rebuilding requires resources, international support, and resolving war crimes and accountability issues.
- Implementation: Ceasefire deals often falter. Ensuring both sides adhere to the agreement is a major challenge.
About Gaza War:
The Gaza War was ignited on October 7, 2023, when Hamas militants launched a surprise multi-front assault on Israel, resulting in the deaths of approximately 1,200 people.
· In response, Israel launched a massive military counteroffensive aimed at destroying Hamas, securing the release of hostages, and ensuring national security.
· The conflict also saw significant regional escalations, including cross-border fighting with Hezbollah and a direct attack by Iran on Israel.
· After two years of devastating conflict, a U.S.-brokered peace plan culminated in a ceasefire in October 2025, including the release of all remaining living hostages held by Hamas, marking a critical step toward stabilizing the region.
Conclusion:
The Gaza declaration and the release of hostages mark a significant turning point in one of the most intractable conflicts of recent years. Yet, this is not an end but a fragile beginning. The real test will be in implementation — ensuring lives saved, dignity restored, and a long‑term, just peace for both Israelis and Palestinians.