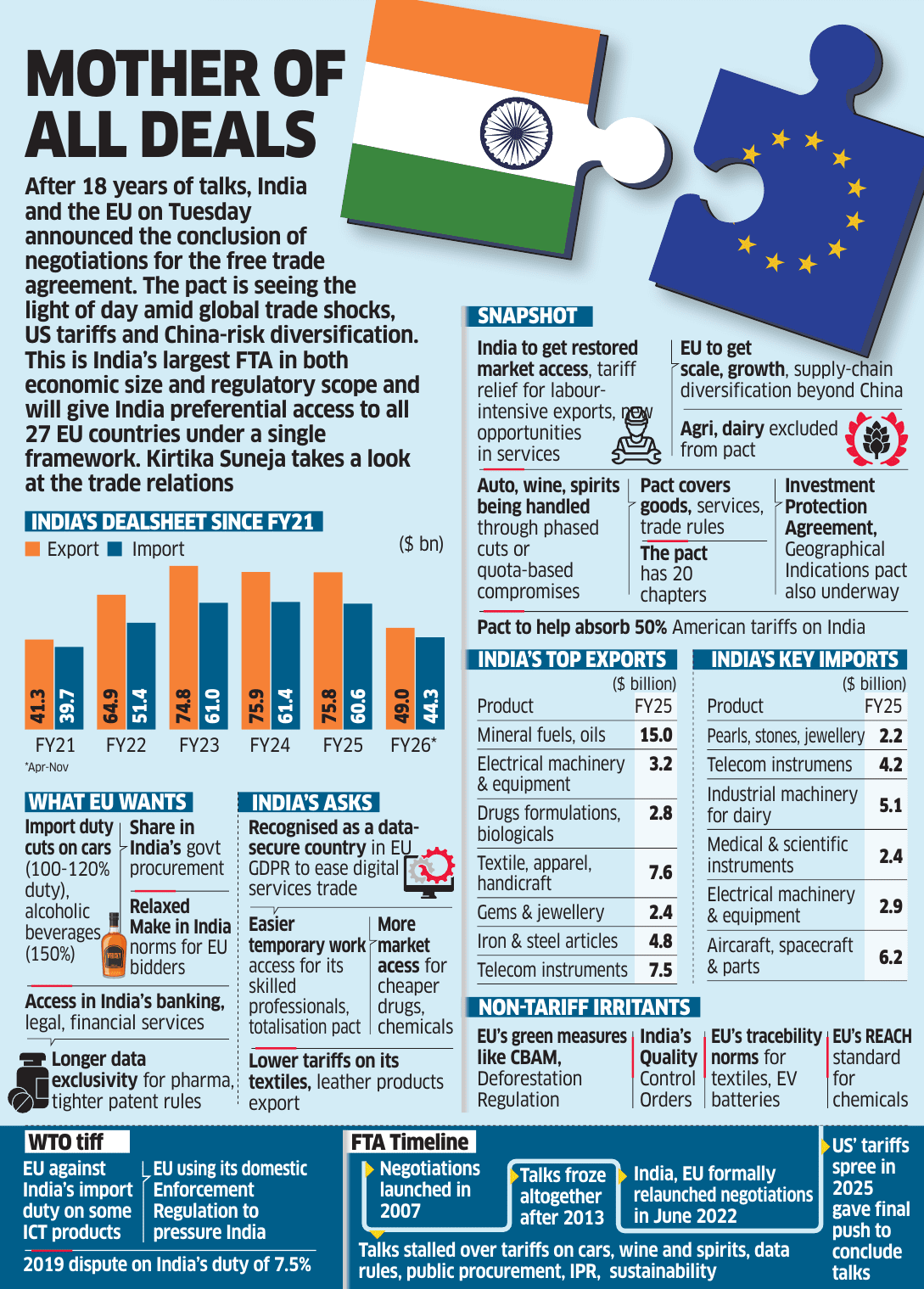
Context:
Recently, India and the European Union (EU) have finalised a landmark Free Trade Agreement (FTA) after nearly two decades of negotiations.
Key Features of the Deal:
1. Tariff Elimination on Goods
-
-
-
- Tariffs on approximately 96–99% of trade by value will be phased down or eliminated over time.
- Duties on EU-made automobiles could be reduced from up to 110% to around 10%, subject to quota limits.
- Tariffs on products such as wine, beer, and olive oil will see significant reductions.
- Tariffs on approximately 96–99% of trade by value will be phased down or eliminated over time.
-
-
2. Services Liberalisation
-
-
-
- European firms will gain enhanced market access in sectors such as financial services and maritime services.
- European firms will gain enhanced market access in sectors such as financial services and maritime services.
-
-
3. Exclusions and Safeguards
-
-
-
- Certain sensitive agricultural products, such as sugar and selected dairy items, remain excluded to protect domestic interests.
- Certain sensitive agricultural products, such as sugar and selected dairy items, remain excluded to protect domestic interests.
-
-
Background:
The idea of an India–EU FTA was first proposed in 2007 but stalled for several years due to differences over market access, tariff levels, and non-tariff barriers. A significant gap in expectations on both sides delayed progress for over a decade. Negotiations resumed in 2022 with renewed political momentum, culminating in a political agreement in 2026.
Benefits and Implications:
For India:
-
-
-
- Export Expansion: Indian sectors such as textiles, leather, chemicals, gems and jewellery, and marine products will gain improved access to EU markets, potentially leading to a substantial increase in exports.
- Enhanced Competitiveness: Reduced EU tariffs will make Indian products more competitive in European markets, helping reverse trade share losses to competitors such as Bangladesh and Vietnam.
- Deeper Integration into Global Value Chains: Improved access to advanced European inputs and technologies could strengthen India’s manufacturing capabilities and export performance.
- Services and Investment Flows: Indian firms will benefit from better access to EU services markets, while European investment is likely to increase in India’s expanding economy.
- Export Expansion: Indian sectors such as textiles, leather, chemicals, gems and jewellery, and marine products will gain improved access to EU markets, potentially leading to a substantial increase in exports.
-
-
For the European Union:
-
-
-
- Access to India’s Large Market: The EU gains tariff relief and expanded access to a rapidly growing consumer market of nearly 1.4 billion people.
- Export Growth and Duty Savings: EU exporters are expected to save up to €4 billion annually in duties as trade barriers are reduced.
- Services Gains and Regulatory Cooperation: European firms stand to benefit from stronger intellectual property protections and eased market entry in financial and professional services.
- Access to India’s Large Market: The EU gains tariff relief and expanded access to a rapidly growing consumer market of nearly 1.4 billion people.
-
-
Strategic and Geopolitical Impact:
-
-
- The agreement strengthens India’s trade diversification strategy amid global trade tensions and rising protectionism in several major economies.
- It signals a deepening strategic partnership between India and the EU at a time of significant geopolitical uncertainty.
- The agreement strengthens India’s trade diversification strategy amid global trade tensions and rising protectionism in several major economies.
-
Challenges and Considerations:
-
-
- Ratification Process: The agreement requires approval by EU member states and Indian authorities before it can enter into force.
- Agricultural Sensitivities: Limited liberalisation in agriculture reflects domestic political, economic, and social considerations.
- Adjustment Pressures: Certain Indian industries may face short-term competitive pressures from EU imports, necessitating supportive policy measures.
- Ratification Process: The agreement requires approval by EU member states and Indian authorities before it can enter into force.
-
Conclusion:
The India–EU Free Trade Agreement represents a historic milestone in trade and diplomacy. It enhances India’s export potential, competitiveness, and global economic integration, while opening the EU to one of the world’s fastest-growing markets. Once ratified, the agreement has the potential to reshape trade flows, economic strategies, and geopolitical alignments over the coming decade.