Context:
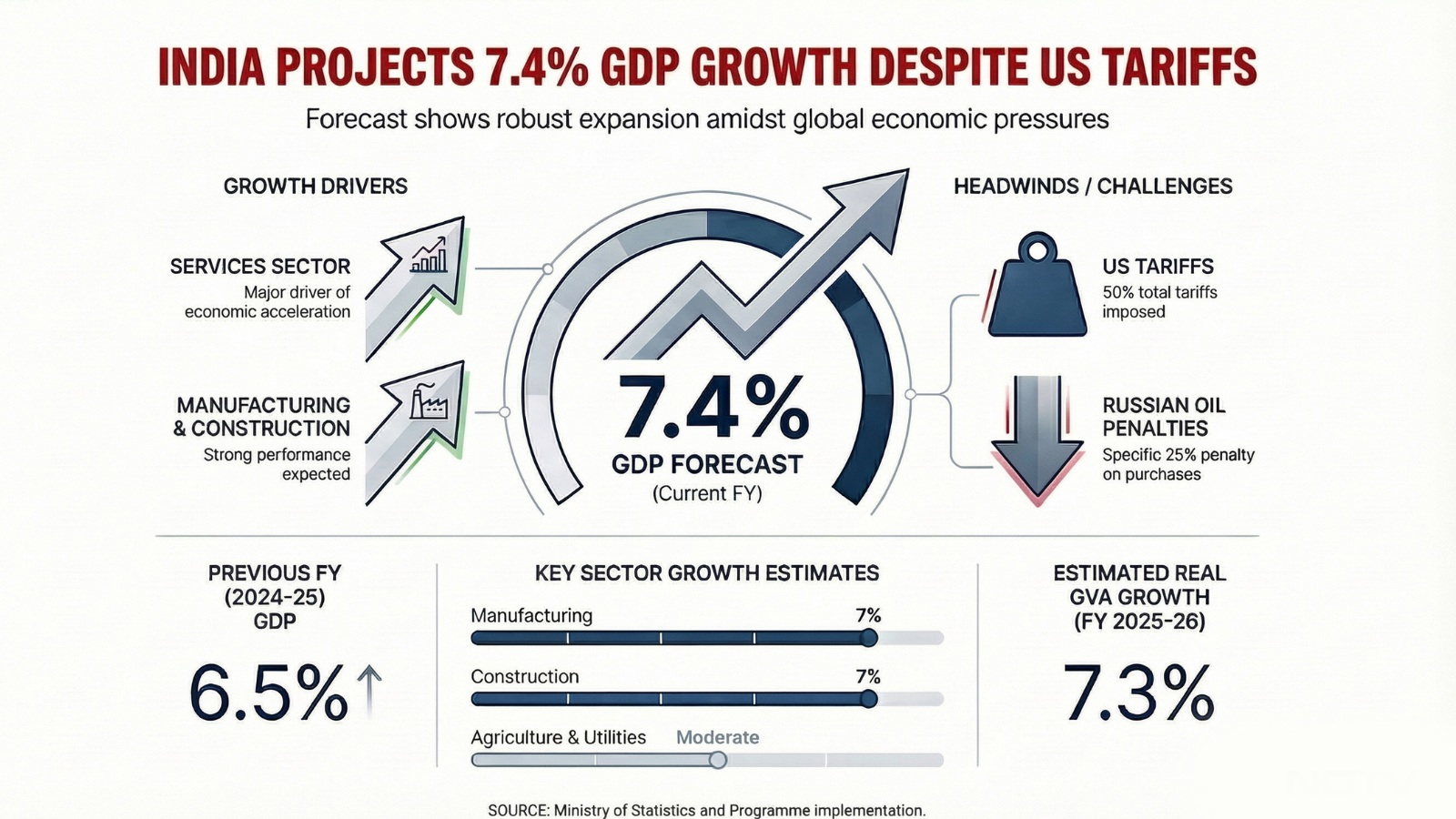
Recently, the first advance estimates of Gross Domestic Product (GDP) released by the Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation (MoSPI) projected that India’s real GDP is expected to grow by 7.4% in the financial year 2025–26 (April 2025–March 2026). This marks a notable acceleration from the 6.5% growth recorded in FY 2024–25. Real GDP at constant (2011–12) prices is estimated to reach approximately ₹201.90 lakh crore in FY 2025–26, compared to ₹187.97 lakh crore in the previous year.
Key Drivers of Growth:
-
-
- Sectoral Contributions
- Services Sector: The services sector continues to be the primary engine of growth, supported by strong performance in trade, hotels, transport, communication, and broadcasting-related services. Robust domestic demand and consumption have underpinned this expansion.
- Manufacturing and Industry: Manufacturing and construction activities in the secondary sector are estimated to grow at around 7%, reflecting sustained industrial activity and ongoing infrastructure development.
- Agriculture: Agricultural growth remains relatively modest, estimated at around 3.1% in FY 2025–26, influenced by climatic conditions and seasonal output variations.
- Services Sector: The services sector continues to be the primary engine of growth, supported by strong performance in trade, hotels, transport, communication, and broadcasting-related services. Robust domestic demand and consumption have underpinned this expansion.
- Other Growth Factors:
- Nominal GDP Growth: Nominal GDP is estimated to expand by approximately 8%, indicating moderate inflationary pressures and subdued price effects.
- Domestic Demand: Sustained private consumption and investment, along with buoyant demand in the services sector, continue to support the overall growth outlook.
- Resilience to External Headwinds: Despite global challenges—such as trade tensions, tariff pressures, and geopolitical uncertainties—India’s strong domestic economic drivers have helped cushion the impact of external shocks.
- Nominal GDP Growth: Nominal GDP is estimated to expand by approximately 8%, indicating moderate inflationary pressures and subdued price effects.
- Sectoral Contributions
-
Economic Significance:
-
-
- Global Context: With a projected growth rate of 7.4%, India is expected to retain its position as one of the fastest-growing major economies globally, outperforming many peer economies. This remains significant even as international financial institutions, including the IMF and the World Bank, offer relatively moderate projections for global and Indian economic growth.
- Policy Implications: The advance estimates serve as a crucial input for the forthcoming Union Budget (FY 2026–27), influencing revenue and expenditure projections, fiscal deficit calculations, and sectoral allocations. Careful policy calibration will be essential to sustain growth while managing inflation and ensuring investment sustainability.
- Global Context: With a projected growth rate of 7.4%, India is expected to retain its position as one of the fastest-growing major economies globally, outperforming many peer economies. This remains significant even as international financial institutions, including the IMF and the World Bank, offer relatively moderate projections for global and Indian economic growth.
-
Challenges and Risks:
Despite the optimistic outlook, economists highlight several potential risks:
-
-
- External Risks: Global trade disruptions, tariff barriers, and geopolitical instability may adversely affect exports and capital flows.
- Nominal Growth Constraints: Lower nominal GDP growth of around 8% may constrain fiscal revenue buoyancy, impacting government expenditure capacity.
- Structural Constraints: Persistent issues such as low agricultural productivity, labour market rigidities, and limited credit access for MSMEs require continued structural reforms and policy intervention.
- External Risks: Global trade disruptions, tariff barriers, and geopolitical instability may adversely affect exports and capital flows.
-
Conclusion:
The Government’s advance estimate of 7.4% real GDP growth in FY 2025–26 underscores India’s strong macroeconomic fundamentals, buoyant services sector, steady industrial expansion and resilient domestic demand. While structural and external challenges remain, the projected growth trajectory provides a favourable foundation for policy planning, economic reforms, and India’s continued rise in the global economic landscape.