Context:
The Health Department in Kozhikode, Kerala, has issued an alert following three reported cases and one death due to Primary Amoebic Meningoencephalitis (PAM), a rare but often fatal brain infection caused by the Naegleria fowleri amoeba.
What is PAM?
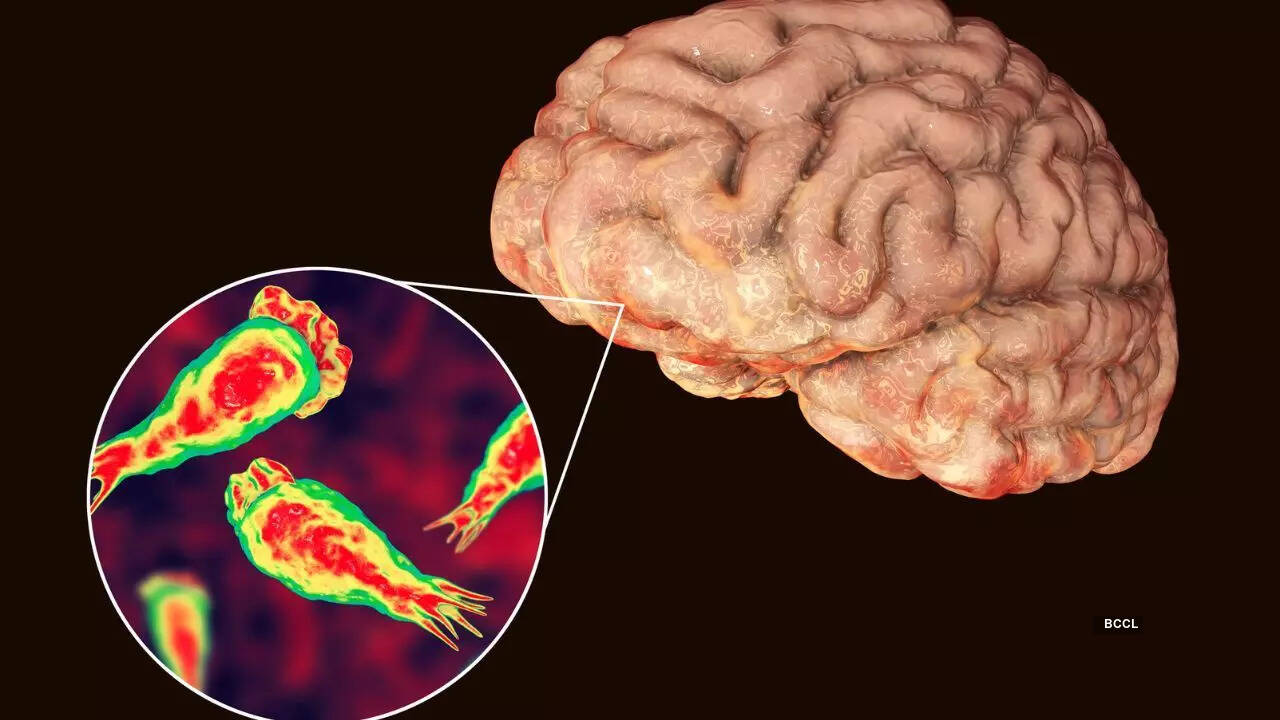
Primary Amoebic Meningoencephalitis (PAM) is a rare but nearly always fatal brain infection caused by Naegleria fowleri, commonly known as the “brain-eating amoeba.” This condition affects the central nervous system, particularly the brain and surrounding membranes.
Cause and Mode of Infection:
· Naegleria fowleri is a free-living amoeba found in warm freshwater bodies like lakes, ponds, rivers, and hot springs.
· Infection occurs when contaminated water enters the nose, usually during swimming or bathing.
· From there, the amoeba travels along the olfactory nerve to the brain, where it causes rapid and devastating tissue damage.
Symptoms and Risk Factors:
· Symptoms appear within 5–10 days and include headache, fever, nausea, vomiting, stiff neck, and light sensitivity.
· As the condition worsens, patients may experience epilepsy, fainting, and memory loss.
· Children may show changes in behavior, such as refusing food or remaining motionless.
Treatment and Prevention:
Amphotericin B and other anti-amoebic drugs have been used, with very few survivors.
Prevention is key: avoid swimming in warm stagnant water, especially during summer, and use nose clips if exposure is unavoidable.
About Brain Infections:
Brain infections, or Central Nervous System (CNS) infections, occur when pathogens like bacteria, viruses, fungi, or parasites invade the brain or its protective structures. These infections lead to inflammation and damage, affecting brain function and overall health.
Types of Brain Infections:
· Meningitis: Inflammation of the meninges, caused by viruses, bacteria, fungi, or parasites. Bacterial meningitis is a medical emergency.
· Encephalitis: Inflammation of brain tissue, usually viral or autoimmune.
· Brain Abscess: Localized pus-filled infection, often bacterial or fungal.
· Subdural Empyema: Infection with pus between dura mater and brain.
· Tuberculomas: Tuberculosis-caused granulomas in the brain.
· Localized Infections: Cysts from fungi, protozoa, or parasites.
· Autoimmune Encephalitis: Immune system attacks brain cells.
· Others: Ventriculitis, cerebritis, NMOSD, prion diseases (TSEs), toxoplasmosis.
Conclusion:
The recent cases of amoebic meningoencephalitis in Kozhikode serve as a stark reminder of the importance of water safety and hygiene. As the health department works to contain the spread of the infection, it is crucial for individuals to take precautions to protect themselves and their loved ones.