Context:
The Alaska Summit 2025, held on August 15 in Anchorage, marked the first meeting between US President Donald Trump and Russian President Vladimir Putin since the Ukraine war began in 2022. Convened amid escalating conflict and global security concerns, the summit ended without a ceasefire, highlighting enduring divisions but signaling a rare reopening of dialogue between Washington and Moscow.
Significance of the Alaska Summit 2025:
o The Alaska Summit was the first meeting between US and Russian leaders on American soil since 1988.
o Central theme was exploring pathways to end the Ukraine conflict.
o The US perspective emphasized the destabilizing impact of the war on European security, NATO unity, and transatlantic relations.
o The Russian position sought international recognition of its territorial control in Ukraine.
· Outcome & Broader Implications
o No breakthrough or ceasefire agreement was reached, reflecting entrenched positions.
o However, the outcome holds potential consequences for:
§ Global geopolitics – recalibration of US-Russia relations, influence on multipolarity debates.
§ Energy markets – continued volatility in oil and gas supplies due to prolonged conflict.
§ Trade relations – sanctions regime may see revisions, impacting global supply chains.
§ NATO cohesion – the alliance may further consolidate against Russia.
· Diplomatic Significance
o Re-established direct channels of communication between Washington and Moscow after years of hostility.
o Both leaders agreed to continue talks, keeping the possibility of future negotiations alive.
Russia-Ukraine War:
· Historical Context
o The roots of the conflict go back to the collapse of the Soviet Union in 1991.
o Ukraine, as a former Soviet republic, has remained strategically significant as a buffer state between Russia and Western Europe.
o Ukraine’s post-independence tilt towards NATO and the European Union has consistently been viewed by Russia as encroachment into its sphere of influence.
· Escalation Since 2014
o Russia’s annexation of Crimea in 2014 marked a turning point, drastically worsening ties.
o The conflict in Eastern Ukraine further deepened mistrust.
o Diplomatic efforts, including the Minsk Agreements, failed to create sustainable peace.
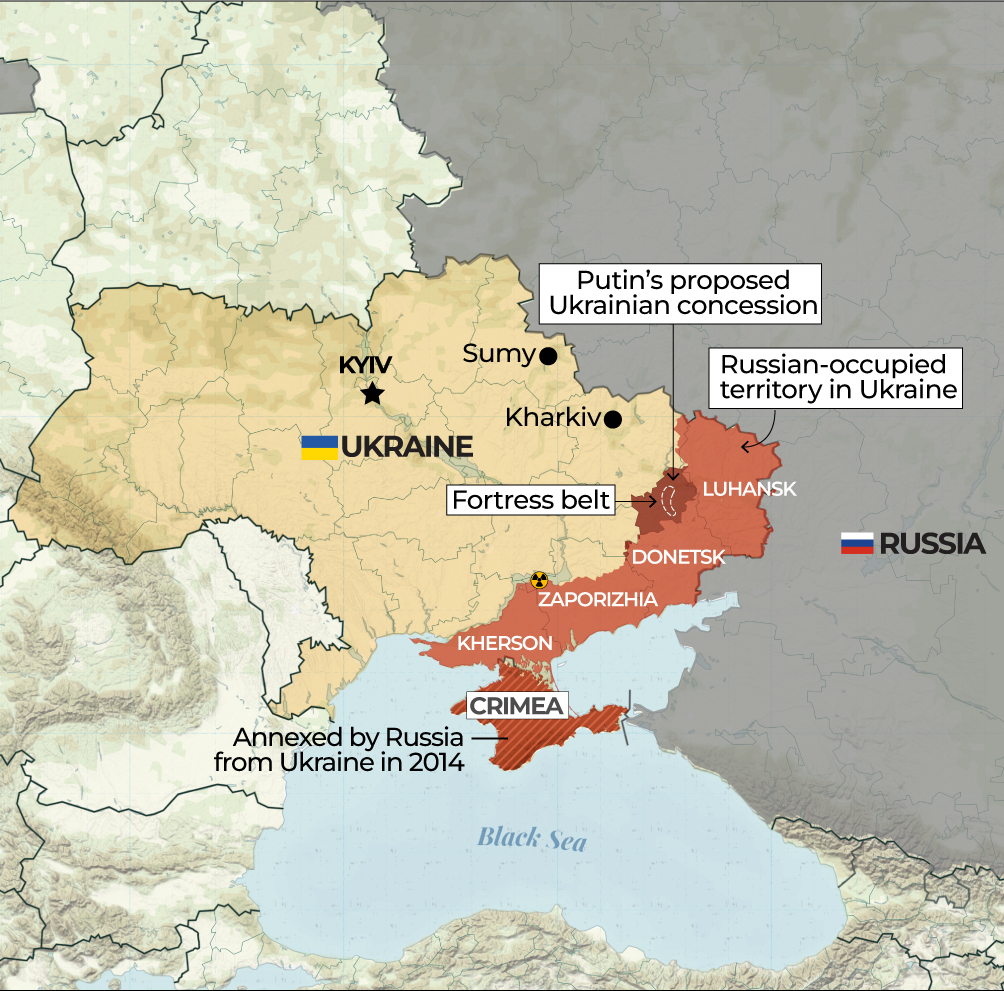
Causes of the 2022 War:
· Underlying Factors
o Russia’s claim over Ukraine as part of its historical and geopolitical sphere of influence.
o Strong resistance to Ukraine’s deepening alignment with the West and NATO aspirations.
· Russian Justification
o Moscow framed the invasion as a mission to “demilitarize” and “denazify” Ukraine.
· Key Drivers of Conflict
o NATO expansion fears and Russia’s security anxieties.
o Ukraine’s moves toward closer ties with Western institutions.
o Putin’s strategic ambition to reassert Russian power and influence in Eastern Europe.
o Continuation of tensions since the 2014 annexation of Crimea.
Global Implications of the War:
· Sanctions & Economic Measures
o Western nations imposed sweeping sanctions targeting Russia’s economy, financial system, and elites.
o Simultaneously, large-scale military and financial aid was directed to Ukraine.
· Global Crises Triggered
o Severe energy crisis, with disruptions in oil and gas supplies.
o Food insecurity worsened by reduced grain exports from the Black Sea region.
o Humanitarian emergency, with millions displaced and large-scale civilian casualties.
· Diplomatic Efforts
o Multiple attempts at mediation, including:
§ UN appeals for ceasefire and humanitarian corridors.
§ Turkey’s mediation in brokering limited agreements such as the Black Sea grain deal.
§ NATO’s recalibrated strategies to bolster deterrence in Eastern Europe.
Conclusion:
The Alaska Summit may not have delivered peace, but it served as a reminder of diplomacy’s dual nature—part negotiation, part theatre. In global affairs, even failed summits have strategic value, influencing public perception, alliances, and the path of future negotiations.







