Brain-booster
/
14 Jul 2023
Brain Booster for UPSC & State PCS Examination (Topic: Increasing Millet Production and Procurement)
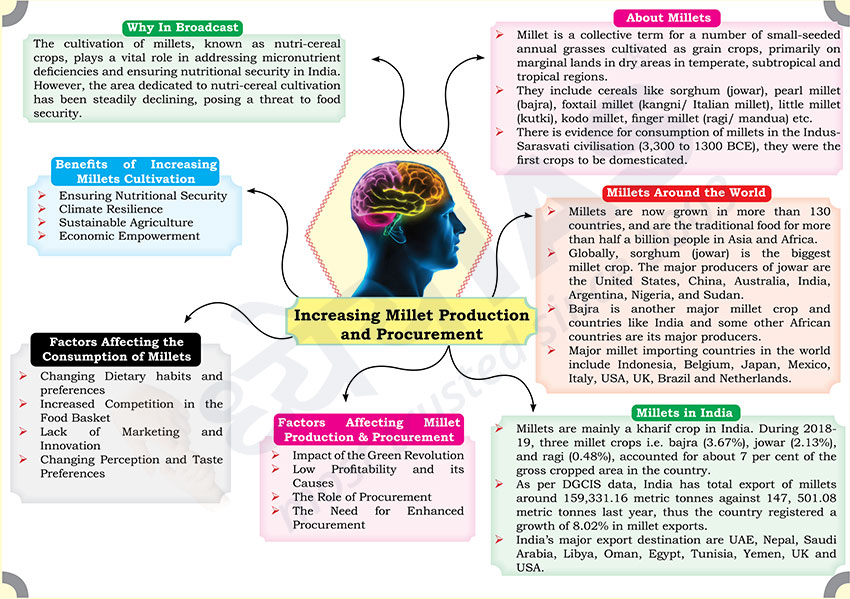
Why in Broadcast?
- The cultivation of millets, known as nutri-cereal crops, plays a vital
role in addressing micronutrient deficiencies and ensuring nutritional
security in India. However, the area dedicated to nutri-cereal cultivation
has been steadily declining, posing a threat to food security.
About Millets
- Millet is a collective term for a number of small-seeded annual grasses
cultivated as grain crops, primarily on marginal lands in dry areas in
temperate, subtropical and tropical regions.
- They include cereals like sorghum (jowar), pearl millet (bajra), foxtail
millet (kangni/ Italian millet), little millet (kutki), kodo millet, finger
millet (ragi/ mandua) etc.
- There is evidence for consumption of millets in the Indus-Sarasvati
civilisation (3,300 to 1300 BCE), they were the first crops to be
domesticated.
Millets Around the World
- Millets are now grown in more than 130 countries, and are the
traditional food for more than half a billion people in Asia and Africa.
- Globally, sorghum (jowar) is the biggest millet crop. The major
producers of jowar are the United States, China, Australia, India,
Argentina, Nigeria, and Sudan.
- Bajra is another major millet crop and countries like India and some
other African countries are its major producers.
- Major millet importing countries in the world include Indonesia,
Belgium, Japan, Mexico, Italy, USA, UK, Brazil and Netherlands.
Millets in India
- Millets are mainly a kharif crop in India. During 2018-19, three millet
crops i.e. bajra (3.67%), jowar (2.13%), and ragi (0.48%), accounted for
about 7 per cent of the gross cropped area in the country.
- As per DGCIS data, India has total export of millets around 159,331.16
metric tonnes against 147, 501.08 metric tonnes last year, thus the country
registered a growth of 8.02% in millet exports.
- India’s major export destination are UAE, Nepal, Saudi Arabia, Libya,
Oman, Egypt, Tunisia, Yemen, UK and USA.
Factors Affecting Millet Production & Procurement
- Impact of the Green Revolution
- Low Profitability and its Causes
- The Role of Procurement
- The Need for Enhanced Procurement
Factors Affecting the Consumption of Millets
- Changing Dietary habits and preferences
- Increased Competition in the Food Basket
- Lack of Marketing and Innovation
- Changing Perception and Taste Preferences
Benefits of Increasing Millets Cultivation
- Ensuring Nutritional Security
- Climate Resilience
- Sustainable Agriculture
- Economic Empowerment







