Context
A recent study published in The Lancet highlights a concerning trend for India’s healthcare between 2010 and 2019. While many countries made significant progress in reducing deaths from non-communicable diseases (NCDs), India saw a rise in mortality rates from these chronic conditions. The study tracked global progress on NCD-related deaths across 185 countries.
Key Findings Related to India:
Between 2010 and 2019, India experienced an increase in the risk of dying from NCDs, particularly among women and older adults.
· The probability of Indian women dying from NCDs rose from 46.6% in 2011 to 48.7% in 2019.
· In 1990, NCDs accounted for 37.9% of deaths, but by 2018, this figure had increased to 63%.
· Heart disease and diabetes are now leading causes of death in India, with both conditions showing a steady rise in fatalities, signaling the urgent need for action in prevention and management.
A Global Comparison:
Globally, the study found that 152 of 185 countries saw a decline in NCD death rates for women, and 147 countries experienced similar trends for men.
· Countries such as Denmark, the United States, China, and Brazil made significant strides in combating chronic diseases.
· In contrast, India and Papua New Guinea were among the few nations where NCD mortality worsened, highlighting India’s growing health challenge.
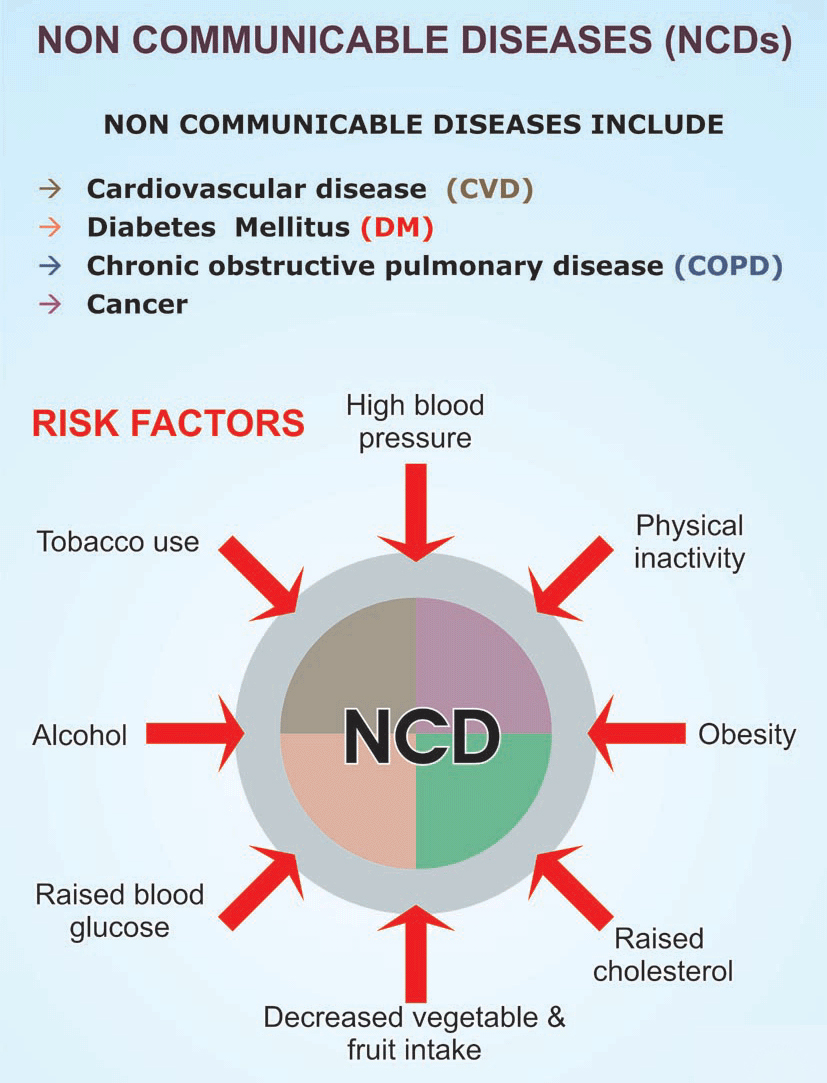
About Non-Communicable Diseases (NCDs):
Non-communicable diseases are chronic conditions that are not transmitted from one person to another. They include:
· Cardiovascular Diseases: Heart attacks, strokes, and hypertension.
· Cancers: Lung, breast, cervical, and colorectal cancers.
· Chronic Respiratory Diseases: COPD and asthma.
· Diabetes: A rising concern due to changing lifestyles.
Causes of NCDs in India:
Several factors contribute to the rise of NCDs in India, including:
1. Lifestyle Factors: Poor diet, lack of physical activity, tobacco and alcohol consumption, and stress.
2. Societal Factors: Urbanization, an aging population, and poverty that exacerbate unhealthy lifestyles.
3. Environmental Factors: Air pollution, both ambient and indoor, along with limited access to healthcare in rural areas.
Initiatives for NCDs in India:
India has launched several initiatives to tackle NCDs:
1. Eat Right India Movement by FSSAI: Promotes healthy eating habits.
2. Fit India Movement(2019): Encourages a physically active lifestyle.
3. National Programme for Prevention and Control of NCDs (NP-NCD): Focuses on early diagnosis and treatment.
4. Ayushman Bharat – PM-JAY(2018): A health insurance scheme aimed at making healthcare more affordable.
Conclusion:
India’s rising chronic disease deaths amidst a global decline underline the need for urgent reforms in public health. Addressing gender disparities, enhancing healthcare infrastructure, and improving data collection are essential steps to curb this growing epidemic and reduce the burden of NCDs in the country.