Context:
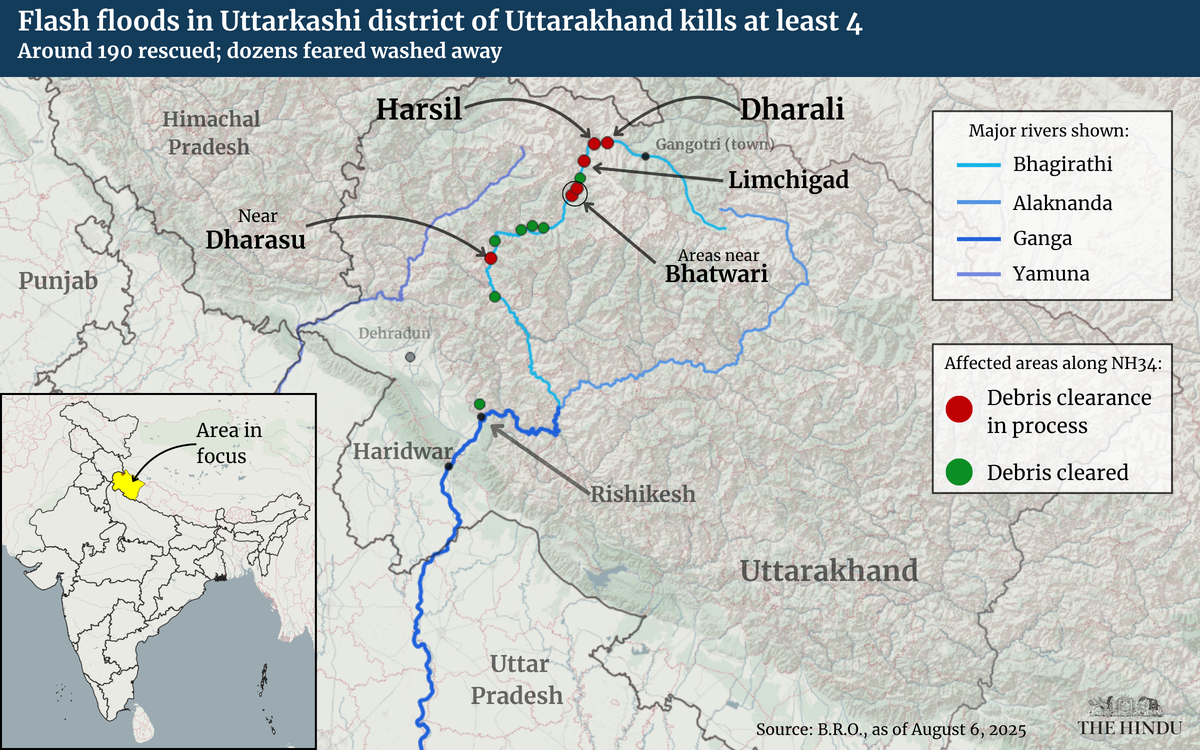
On August 5, 2025, flash floods and mudslides hit the Dharali village in Uttarkashi district, Uttarakhand, resulting in the loss of at least four lives and extensive damage to buildings, shops, and hotels. While flash floods are not uncommon in the hilly regions of Uttarakhand, the cause of this particular disaster lies in a combination of the region's unique topography and heavy, continuous rainfall.
What caused flash flood in the Uttarkashi district:
The flash floods in Uttarkashi were caused by a combination of factors:
1. Heavy Rainfall: Continuous rainfall over several days saturated the ground, increasing runoff and leading to flash floods, even though it wasn’t a "cloudburst."
2. Rugged Topography: The steep, mountainous terrain and deep valleys caused rainwater to rapidly flow downhill, gaining momentum and triggering floods.
3. Landslides and Mudslides: Heavy rain loosened the soil, causing debris to flow into rivers and streams, further increasing water flow.
4. Climate Change: Accelerated melting of glaciers due to climate change added more water to already swollen rivers, heightening flood risks.
5. Lack of Vegetation: Limited vegetation made it harder for the soil to absorb water, causing rainwater to flow quickly downhill, contributing to flash floods.
What Are Flash Floods?
Flash floods are sudden, rapid floods that occur within a short period, usually within six hours of intense rainfall or other water accumulation events. They can cause swift rises in water levels in rivers, streams, or urban areas, often with little warning.
Causes of Flash Floods:
Flash floods can result from heavy rainfall, dam failures, debris jams, or the sudden release of water from natural reservoirs like glacial lakes. In India, flash floods are frequently linked to cloudbursts, which involve intense rainfall over a short duration. Factors like the steepness of terrain, soil type, and human-made barriers also contribute to flash floods.
Features of Flash Floods:
Flash floods are characterized by their high intensity, carrying large volumes of water, debris, and sediment.
· They can overwhelm drainage systems, cause Rivers to overflow, and inundate low-lying areas.
· Flash floods are more common in narrow, steep rivers or urban areas where concrete prevents water absorption.
Difference from Regular Floods:
· Flash floods develop rapidly, often within hours, while regular floods occur gradually over days or weeks.
· Flash floods are more intense but short-lived, whereas regular floods can last for longer periods.
· Flash floods offer little warning time, while regular floods usually allow more time for evacuation.
Mitigating Flash Floods:
Early warning systems, such as weather monitoring and river gauges, play a crucial role in minimizing damage. In India, agencies like IMD use Doppler radars for flash flood forecasting, while the NDMA advises regulation of habitation in flood-prone areas.
Conclusion:
The flash floods in Uttarkashi on August 5, 2025, highlight the vulnerability of the region's unique topography, which makes it prone to disasters such as landslides, debris flows, and flash floods. The continuous heavy rainfall, compounded by climate change, created the perfect conditions for such an event. This tragic event underscores the need for proactive measures, such as better early warning systems, infrastructure resilience, and the restoration of vegetation to prevent further destruction in such vulnerable regions.