Date : 24/10/2023
Relevance:GS Paper 2 - Social Justice, Government Inventions
GS Paper 3 – Science and Technology
Keywords:The Lancet, HPV, National Cancer Awareness Day, National Cancer Grid
Context-
A recent research study by The Lancet Regional Health Southeast Asia has highlighted substantial regional differences in the survival rates of individuals diagnosed with cervical cancer throughout India.
Key Findings of the Study
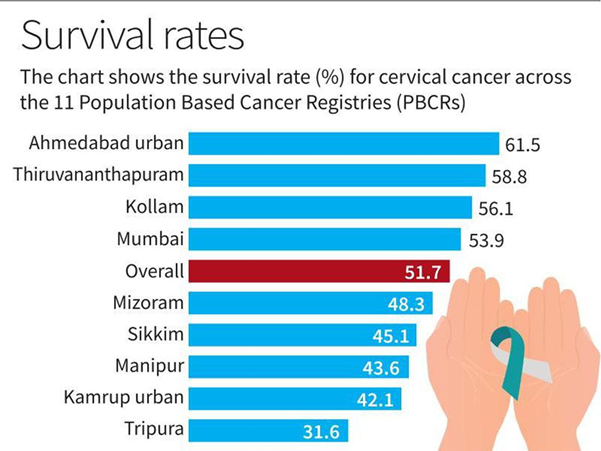
- Survival Rate:
Between 2012 and 2015, approximately 52% of cervical cancer cases diagnosed during that period survived. - Variations Across Regions:
The study participants revealed varying survival rates across different regions of India. Notably, Ahmedabad urban registry exhibited the highest survival rate at 61.5%, followed by Thiruvananthapuram with 58.8% and Kollam at 56.1%. In contrast, Tripura reported a considerably lower survival rate of 31.6%. - Factors Responsible for Regional Disparities:
The research highlighted several factors contributing to the regional disparities in survival rates, including access to diagnostic services, effectiveness of treatment, distance from healthcare facilities, travel costs, co-morbidities, and poverty.
Understanding Cervical Cancer
Cervical cancer, originating in a woman's cervix (the entrance to the uterus from the vagina), is predominantly caused by high-risk human papillomaviruses (HPV) transmitted through sexual contact. Specifically, HPV types 16 and 18 are responsible for nearly half of high-grade cervical pre-cancers. It's important to note that cervical cancer ranks as the fourth most common cancer among women globally. Alarmingly, around 90% of new cases and deaths in 2020 occurred in low- and middle-income countries.
Comprehensive Cervical Cancer Control
Effective cervical cancer control strategies encompass various stages:
- Primary Prevention: This involves vaccination against HPV, the primary cause of cervical cancer.
- Secondary Prevention: This includes screening and treatment of pre-cancerous lesions, aiming to detect and address abnormalities before they progress.
- Tertiary Prevention: Involves the diagnosis and treatment of invasive cervical cancer, focusing on managing advanced stages of the disease.
- Palliative Care: Ensures that patients receive supportive and comforting care, especially in cases where the cancer is advanced and cannot be cured.
Government Initiatives in Cancer Treatment
1. National Programme for Prevention and Control of Cancer, Diabetes, Cardiovascular Diseases, and Stroke:The government has implemented a comprehensive program aimed at preventing and controlling diseases such as cancer, diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, and stroke.
2. National Cancer Grid:The National Cancer Grid is an initiative fostering collaboration among cancer centers, promoting standardized cancer care and research across India.
3. National Cancer Awareness Day:Recognizing the importance of awareness, the government observes National Cancer Awareness Day to educate the public about cancer prevention, early detection, and available treatments.
4. HPV Vaccine:The government has introduced vaccination programs, including the HPV vaccine, to protect against human papillomavirus infections, a leading cause of cervical cancer.
Challenges Faced by Healthcare Providers in Curing Cancer
1. Heterogeneity of Cancer:
Cancer encompasses a diverse group of diseases, each requiring a specific approach, making a universal cure challenging.
2. Late Diagnosis:
Advanced-stage diagnoses reduce curative possibilities; lack of early detection methods and public awareness compounds the issue.
3. Treatment Toxicity:
Traditional treatments like chemotherapy often cause severe side effects, affecting patients' quality of life; developing targeted therapies is essential.
4. Resistance to Treatment:
Cancers can develop resistance to treatment, posing a hurdle in finding effective cures; overcoming this resistance is crucial.
5. Cost of Treatment:
High expenses associated with cancer treatments create barriers, especially for economically disadvantaged patients.
6. Lack of Access to Care:
Limited access to cancer facilities, especially in low-income areas, contributes to regional disparities in cancer outcomes.
7. Awareness and Training Gaps:
Lack of patient awareness about rights, schemes, and inadequate training for healthcare providers exacerbate the problem.
8. Limited Availability of Specialized Care:
Specialized cancer care centers are concentrated in urban areas, leaving rural regions underserved.
9. Stigmatization and Fear:
Social stigma and fear often lead to delayed diagnosis and treatment, hindering effective cancer care.
Ways to Reduce Regional Disparities in Cancer Care in India
1. Awareness and Education:
Conduct region-specific awareness campaigns on prevention, early detection, and available treatments in local languages.
2. Preventive Measures:
Encourage healthy lifestyles, discourage tobacco use, and promote regular screenings and vaccinations (e.g., HPV vaccines).
3. Primary Healthcare Strengthening:
Enhance primary healthcare quality and accessibility, creating a network to identify potential cancer cases and refer them appropriately.
4. Telemedicine:
Utilize telemedicine and mobile health units to offer cancer consultations and education in remote areas, enabling expert guidance.
5. Government Initiatives:
Implement well-funded national cancer control programs, building and upgrading treatment centers in underserved regions.
6. Subsidized Treatment:
Provide financial assistance for cancer treatments, particularly for economically disadvantaged patients, through government schemes and insurance programs.
7. Research and Development:
Invest in cancer research and foster innovation for cost-effective treatments and diagnostics, fostering collaborations between government, academia, and the private sector.
8. Community Engagement:
Involve local communities and NGOs in awareness campaigns and support services to combat cultural stigmas and improve access to care.
Conclusion
While regional disparities in cervical cancer survival rates present challenges, India's proactive initiatives and collaborative efforts offer hope. By enhancing awareness, strengthening healthcare infrastructure, embracing technology, and engaging communities, the nation can bridge these gaps. With ongoing dedication to research and accessible, innovative treatments, India is on a promising path to significantly reduce regional disparities in cancer care, ensuring a healthier future for all.
Probable Questions for UPSC Mains exam-
- 1. Discuss the role of government initiatives in combating cervical cancer in India. How can the integration of technology and community engagement further enhance the effectiveness of these initiatives? (10 marks, 150 words)
- 1. Discuss the role of government initiatives in combating cervical cancer in India. How can the integration of technology and community engagement further enhance the effectiveness of these initiatives? (10 marks, 150 words)
Source - The Hindu