Brain-booster
/
23 Dec 2022
Brain Booster for UPSC & State PCS Examination (Topic: Suicide Prevention Strategy)
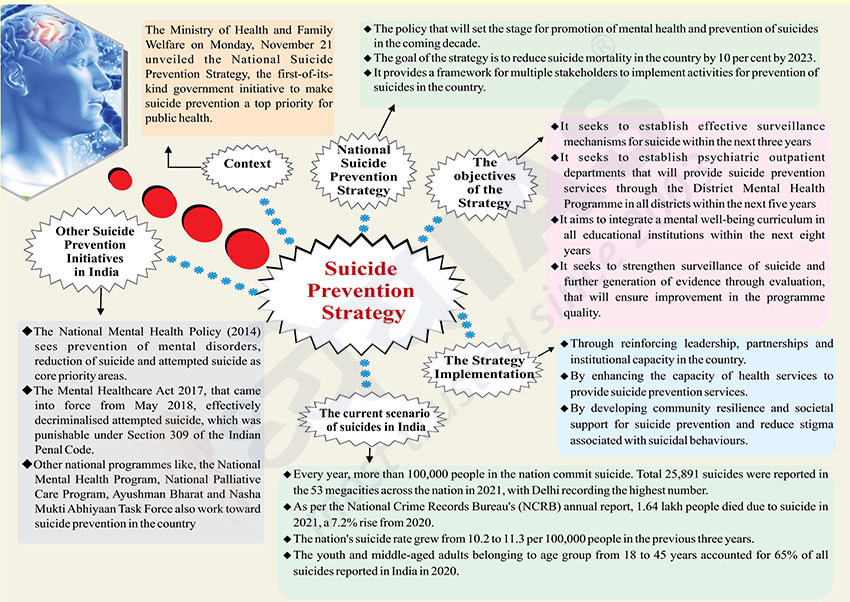
Context
- The Ministry of Health and Family Welfare on Monday, November 21
unveiled the National Suicide Prevention Strategy, the first-of-itskind
government initiative to make suicide prevention a top priority for public
health.
National Suicide Prevention Strategy
- The policy that will set the stage for promotion of mental health and
prevention of suicides in the coming decade.
- The goal of the strategy is to reduce suicide mortality in the country
by 10 per cent by 2023.
- It provides a framework for multiple stakeholders to implement
activities for prevention of suicides in the country.
The objectives of the Strategy
- It seeks to establish effective surveillance mechanisms for suicide
within the next three years
- It seeks to establish psychiatric outpatient departments that will
provide suicide prevention services through the District Mental Health
Programme in all districts within the next five years
- It aims to integrate a mental well-being curriculum in all educational
institutions within the next eight years
- It seeks to strengthen surveillance of suicide and further generation of
evidence through evaluation, that will ensure improvement in the programme
quality.
The Strategy Implementation
- Through reinforcing leadership, partnerships and institutional capacity
in the country.
- By enhancing the capacity of health services to provide suicide
prevention services.
- By developing community resilience and societal support for suicide
prevention and reduce stigma associated with suicidal behaviours.
The current scenario of suicides in India
- Every year, more than 100,000 people in the nation commit suicide. Total
25,891 suicides were reported in the 53 megacities across the nation in
2021, with Delhi recording the highest number.
- As per the National Crime Records Bureau's (NCRB) annual report, 1.64
lakh people died due to suicide in 2021, a 7.2% rise from 2020.
- The nation's suicide rate grew from 10.2 to 11.3 per 100,000 people in
the previous three years.
- The youth and middle-aged adults belonging to age group from 18 to 45
years accounted for 65% of all suicides reported in India in 2020.
Other Suicide Prevention Initiatives in India
- The National Mental Health Policy (2014) sees prevention of mental
disorders, reduction of suicide and attempted suicide as core priority
areas.
- The Mental Healthcare Act 2017, that came into force from May 2018,
effectively decriminalised attempted suicide, which was punishable under
Section 309 of the Indian Penal Code.
- Other national programmes like, the National Mental Health Program,
National Palliative Care Program, Ayushman Bharat and Nasha Mukti Abhiyaan
Task Force also work toward suicide prevention in the country







