Brain-booster
/
15 Nov 2021
Brain Booster for UPSC & State PCS Examination (Topic: Evolution of Indian Constitution Phase - I)
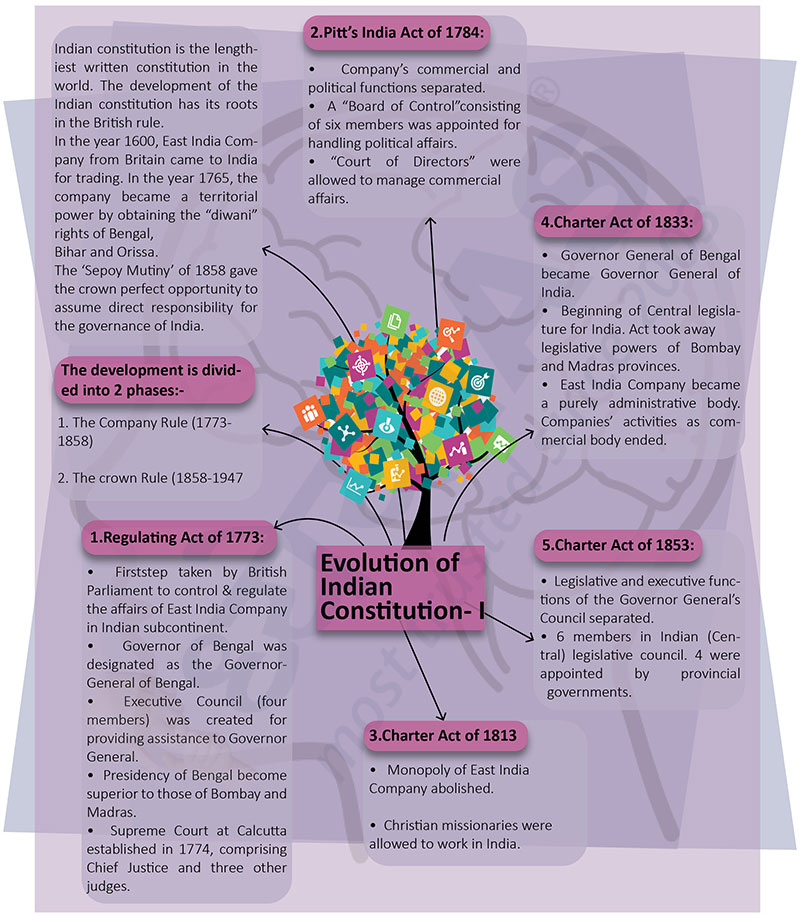
- Indian constitution is the lengthiest written constitution in
the world. The development of the Indian constitution has its roots
in the British rule.
- In the year 1600, East India Company from Britain came to India
for trading. In the year 1765, the company became a territorial
power by obtaining the “diwani” rights of Bengal, Bihar and Orissa.
- The ‘Sepoy Mutiny’ of 1858 gave the crown perfect opportunity to
assume direct responsibility for the governance of India.
The development is divided into 2 phases:
- The Company Rule (1773- 1858)
- The crown Rule (1858-1947)
1. Regulating Act of 1773:
- First step taken by British Parliament to control & regulate the affairs
of East India Company in Indian subcontinent.
- Governor of Bengal was designated as the Governor- General of Bengal.
- Executive Council (four members) was created for providing assistance to
Governor General.
- Presidency of Bengal become superior to those of Bombay and Madras.
- Supreme Court at Calcutta established in 1774, comprising Chief Justice
and three other judges.
2. Pitt’s India Act of 1784:
- Company’s commercial and political functions separated.
- A “Board of Control”consisting of six members was appointed for handling
political affairs.
- “Court of Directors” were allowed to manage commercial affairs.
3. Charter Act of 1813
- Monopoly of East India Company abolished.
- Christian missionaries were allowed to work in India.
4. Charter Act of 1833:
- Governor General of Bengal became Governor General of India.
- Beginning of Central legislature for India. Act took away legislative
powers of Bombay and Madras provinces.
- East India Company became a purely administrative body. Companies’
activities as commercial body ended.
5. Charter Act of 1853:
- Legislative and executive functions of the Governor General’s Council
separated.
- 6 members in Indian (Central) legislative council. 4 were appointed by
provincial governments.







