Brain-booster
/
29 Dec 2022
Brain Booster for UPSC & State PCS Examination (Topic: Carbon Capture, Utilisation, and Storage - CCUS)
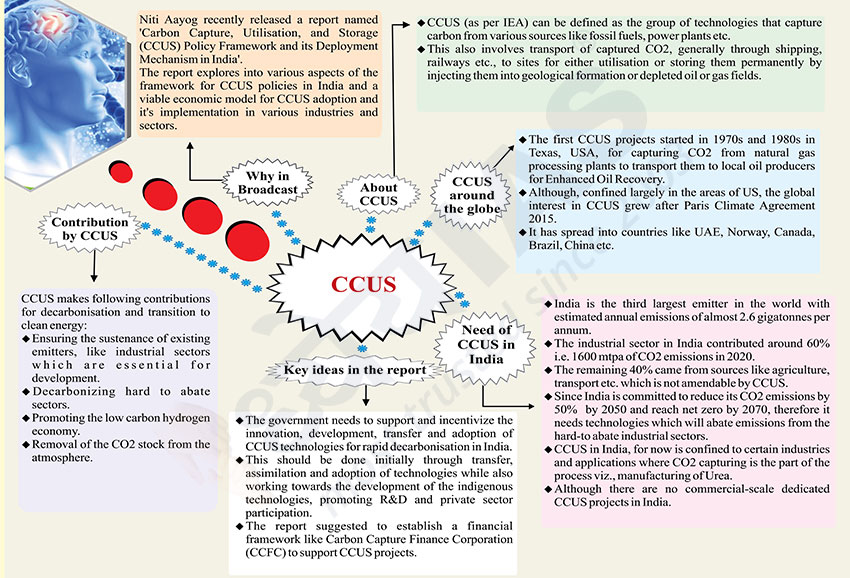
Why in Broadcast?
- Niti Aayog recently released a report named 'Carbon Capture,
Utilisation, and Storage (CCUS) Policy Framework and its Deployment
Mechanism in India'. The report explores into various aspects of the
framework for CCUS policies in India and a viable economic model for CCUS
adoption and it's implementation in various industries and sectors.
About CCUS
- CCUS (as per IEA) can be defined as the group of technologies that
capture carbon from various sources like fossil fuels, power plants etc.
- This also involves transport of captured CO2, generally through
shipping, railways etc., to sites for either utilisation or storing them
permanently by injecting them into geological formation or depleted oil or
gas fields.
CCUS around the globe
- The first CCUS projects started in 1970s and 1980s in Texas, USA, for
capturing CO2 from natural gas processing plants to transport them to local
oil producers for Enhanced Oil Recovery.
- Although, confined largely in the areas of US, the global interest in
CCUS grew after Paris Climate Agreement 2015.
- It has spread into countries like UAE, Norway, Canada, Brazil, China
etc.
Need of CCUS in India
- India is the third largest emitter in the world with estimated annual
emissions of almost 2.6 gigatonnes per annum.
- The industrial sector in India contributed around 60% i.e. 1600 mtpa of
CO2 emissions in 2020.
- The remaining 40% came from sources like agriculture, transport etc.
which is not amendable by CCUS.
- Since India is committed to reduce its CO2 emissions by 50% by 2050 and
reach net zero by 2070, therefore it needs technologies which will abate
emissions from the hard-to abate industrial sectors.
- CCUS in India, for now is confined to certain industries and
applications where CO2 capturing is the part of the process viz.,
manufacturing of Urea.
- Although there are no commercial-scale dedicated CCUS projects in India.
Key ideas in the report
- The government needs to support and incentivize the innovation,
development, transfer and adoption of CCUS technologies for rapid
decarbonisation in India.
- This should be done initially through transfer, assimilation and
adoption of technologies while also working towards the development of the
indigenous technologies, promoting R&D and private sector participation.
- The report suggested to establish a financial framework like Carbon
Capture Finance Corporation (CCFC) to support CCUS projects.
Contribution by CCUS
- CCUS makes following contributions for decarbonisation and transition to
clean energy:
- Ensuring the sustenance of existing emitters, like industrial sectors
which are essential for development.
- Decarbonizing hard to abate sectors.
- Promoting the low carbon hydrogen economy.
- Removal of the CO2 stock from the atmosphere.







