Brain-booster
/
06 Apr 2023
Brain Booster for UPSC & State PCS Examination (Topic: World Water Day 2023)
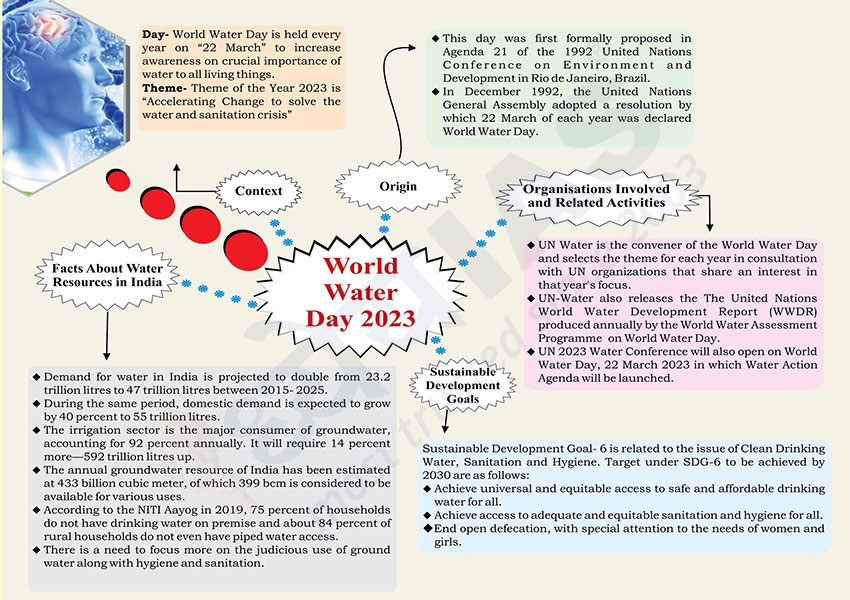
Context
- Day- World Water Day is held every year on “22 March” to increase
awareness on crucial importance of water to all living things.
- Theme- Theme of the Year 2023 is “Accelerating Change to solve
the water and sanitation crisis”
Origin
- This day was first formally proposed in Agenda 21 of the 1992 United
Nations Conference on Environment and Development in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil.
- In December 1992, the United Nations General Assembly adopted a
resolution by which 22 March of each year was declared World Water Day.
Organisations Involved and Related Activities
- UN Water is the convener of the World Water Day and selects the theme
for each year in consultation with UN organizations that share an interest
in that year's focus.
- UN-Water also releases the The United Nations World Water Development
Report (WWDR) produced annually by the World Water Assessment Programme on
World Water Day.
- UN 2023 Water Conference will also open on World Water Day, 22 March
2023 in which Water Action Agenda will be launched.
Sustainable Development Goals
- Sustainable Development Goal- 6 is related to the issue of Clean
Drinking Water, Sanitation and Hygiene. Target under SDG-6 to be achieved by
2030 are as follows:
- Achieve universal and equitable access to safe and affordable
drinking water for all.
- Achieve access to adequate and equitable sanitation and hygiene for
all.
- End open defecation, with special attention to the needs of women
and girls.
Facts About Water Resources in India
- Demand for water in India is projected to double from 23.2 trillion
litres to 47 trillion litres between 2015- 2025.
- During the same period, domestic demand is expected to grow by 40
percent to 55 trillion litres.
- The irrigation sector is the major consumer of groundwater, accounting
for 92 percent annually. It will require 14 percent more—592 trillion litres
up.
- The annual groundwater resource of India has been estimated at 433
billion cubic meter, of which 399 bcm is considered to be available for
various uses.
- According to the NITI Aayog in 2019, 75 percent of households do not
have drinking water on premise and about 84 percent of rural households do
not even have piped water access.
- There is a need to focus more on the judicious use of ground water along
with hygiene and sanitation.







