Date: 22/05/2023
Relevance: GS-3: Biodiversity and Environment
Key Phrases: Climate change impact, Human consumption, Sedimentation, Rising temperatures, Pollution control, Ecosystem disruption.
Context:
- A recent study has revealed that more than half of the world's large lakes and reservoirs have experienced a decrease in size since the early 1990s.
- The research involved analyzing nearly 2,000 large lakes using satellite measurements, climate models, and hydrological models.
Do you know?
- By 2080, the world's lakes will experience a temperature change of up to 6.7c caused by greenhouse gas emissions.
- The Caspian Sea, holds the distinction of being the world's largest lake.
- In 1981, Chilika Lake was designated as the first Indian wetland of international significance.
- In India, the Wular Lake located in Jammu and Kashmir holds the distinction of being the country's largest freshwater lake.
- Chilika Lake, located in the state of Odisha, holds the distinction of being India's largest saltwater lake.
- Udaipur is renowned as the "City of Lakes" in India.
Key Highlights:
- Over 50% decline: The study found that more than half of the world's large lakes and reservoirs have experienced a significant decline in water levels since the early 1990s. This decline poses substantial challenges for water availability and sustainability.
- Climate change impact: Climate change emerged as the primary driver behind the shrinkage of these water bodies. Rising temperatures and changing rainfall patterns play a crucial role in the reduction of lake and reservoir volumes.
- Human consumption: Unsustainable human use of water resources is a significant factor contributing to the decline. Excessive extraction for agriculture, industry, and domestic purposes depletes the water sources, exacerbating the problem.
- Altered rainfall and run-off: Changes in rainfall patterns and increased run-off affect the replenishment of lakes and reservoirs. Reduced rainfall and increased evaporation rates diminish the inflow of water, leading to a decline in water levels.
- Sedimentation: The accumulation of silt and other materials in lakes and reservoirs, reduces their capacity to hold water. This process further contributes to the decline in water levels.
- Important freshwater sources, including the Caspian Sea and Lake Titicaca, have lost water at a cumulative rate of about 22 giga tonnes per year for nearly three decades.
- Positive Changes: Water levels in approximately 25% of the studied lakes have increased, often due to dam construction in remote areas like the Inner Tibetan Plateau.
Role of Climate Change in the Shrinking of Large Lakes and Reservoirs:
- Increased evapotranspiration:
- With rising temperatures, there is an increase in evapotranspiration, which refers to the combined loss of water from both land surfaces and plants.
- This higher evapotranspiration rate further contributes to the depletion of water in lakes and reservoirs.
- Melting glaciers and reduced snowfall:
- Climate change affects mountainous regions, leading to the melting of glaciers and reduced snowfall.
- These changes impact the supply of freshwater to lakes and reservoirs, particularly those reliant on glacier meltwater or snowmelt.
- Altered hydrological cycles:
- Climate change disrupts the natural hydrological cycles, including the timing and duration of wet and dry seasons.
- These alterations affect the inflow and outflow of water, further exacerbating the decline of large lakes and reservoirs.
- Increased frequency of extreme weather events:
- Climate change is associated with more frequent and intense extreme weather events such as droughts, heatwaves, and intense storms.
- These events can lead to rapid water loss through evaporation, increased runoff, or damage to infrastructure, affecting the overall water balance in lakes and reservoirs.
- Changing rainfall patterns:
- Climate change causes uneven distribution of rainfall.
- Reduced precipitation in certain areas or altered timing and intensity of rainfall events impact the inflow of water into lakes and reservoirs.
- Results in decreased replenishment and declining water levels in affected water bodies.
- Areas experiencing reduced rainfall face heightened risks of water scarcity and lake shrinkage.

Implications:
- Water scarcity:
- The decline of large lakes and reservoirs has severe implications for global water resources.
- The reduced availability of freshwater impacts various sectors, including agriculture, energy, and human consumption.
- It exacerbates water scarcity, leading to conflicts and socio-economic challenges.
- Food security:
- Agriculture heavily relies on water resources for irrigation.
- As lakes and reservoirs shrink, the water supply for agricultural activities diminishes, impacting crop yields, food production, and food security.
- This can lead to increased food prices and food shortages.
- Energy generation:
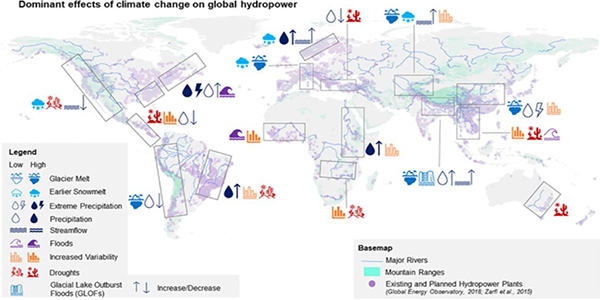
- Many hydropower plants depend on large lakes and reservoirs for water supply.
- The decline in water levels affects hydropower generation, leading to energy shortages and an increased reliance on other energy sources, potentially impacting energy prices.
- Ecosystem disruption:
- Large lakes and reservoirs support diverse ecosystems, and their decline threatens the survival of aquatic plants and animals.
- It disrupts the ecological balance, affecting biodiversity and the overall health of ecosystems.
- Socio-economic impacts:
- The decline of lakes and reservoirs directly affects human populations. Communities relying on these water bodies for drinking water, agriculture, and livelihoods face water shortages, increased competition, and potential migration.
- This poses significant socio-economic challenges, particularly in regions heavily dependent on these water sources.
Significance of Sustainable Human Use in Addressing the Issue:
- Reduction of water demand:
- Unsustainable water consumption practices contribute to the decline of lakes and reservoirs.
- Excessive water extraction for agriculture, industry, and domestic use strains water resources.
- Promoting sustainable human use helps reduce the demand for water, alleviating pressure on these vulnerable water bodies.
- Efficient water management practices:
- Implementing water conservation measures to optimize water use.
- Adoption of responsible irrigation techniques to minimize water wastage.
- Recycling and reuse of water to maximize efficiency.
- Pollution control:
- Minimizing the introduction of harmful substances into lakes and reservoirs.
- Reducing pollution from industrial discharge, agricultural runoff, and untreated wastewater.
- Implementation of wastewater treatment and pollution control measures.
- Long-term sustainability:
- Sustainable human use practices ensure the long-term viability of lakes and reservoirs.
- Balancing water extraction with the natural replenishment capacity of these water bodies.
- Promoting responsible water management practices to maintain ecosystem health and biodiversity.
Conclusion:
- The study's findings underscore the urgent need for sustainable water management and climate change mitigation measures.
- Addressing the factors contributing to the decline of large lakes and reservoirs is crucial for ensuring water security, food production, energy generation, and the well-being of human populations worldwide.
- Effective policies, conservation efforts, and international cooperation are necessary to mitigate the implications and safeguard global water resources.
Source: The Hindu
Mains Question:
Q. Critically analyze the role of climate change in the shrinking of large lakes and reservoirs. Evaluate the significance of sustainable human use in addressing this issue. (250 Words).







