Date : 29/08/2023
Relevance – GS Paper 3 – Environment – Pollutant
Keywords – NHM, CAREH, Heavy metal, lead-acid batteries
Context –
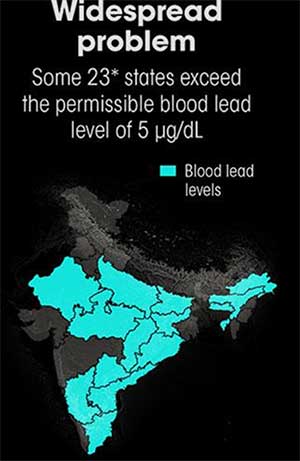
In India, the issue of lead poisoning remains concealed, as studies indicate that more than 50% of children have blood lead levels exceeding the safe limit of 5 micrograms per deciliter (µg/dL) set by the World Health Organization.
About Lead
Lead, a heavy metal element, possesses toxicity to humans and can result in severe health complications upon ingestion or inhalation, particularly in substantial quantities. Prominent avenues of lead exposure encompass lead-containing paints, lead-acid batteries, polluted soil and water, and work-related risks within sectors like mining, smelting, and battery recycling.
What is Lead Poisoning?
Lead poisoning is a medical condition that arises when an individual's body accumulates elevated levels of lead, a harmful metal. This condition can result in a range of health complications, particularly among children, such as learning disabilities, neurological disorders, impaired growth, and damage to vital organs.
Impact of Lead on Children:
- Lead, a powerful neurotoxin, inflicts lasting damage on the developing brains of children.
- Its impact is most profound on infants and kids below 5 years old, affecting their brain development before it matures fully. This leads to enduring neurological, cognitive, and physical impairments that persist throughout their lives.
- Furthermore, childhood exposure to lead has connections to mental health issues, behavioral disorders, and a rise in criminal tendencies and violence.
- For older children, the repercussions are equally dire, including an elevated likelihood of kidney damage and cardiovascular ailments in their later years.
Lead Poisoning Concerns in India:
- Elevated Childhood Exposure: Research in 2021 revealed that approximately 200 million children in India exhibit blood lead levels surpassing WHO's safe threshold.
- Severe Health Consequences: The ramifications of lead poisoning encompass learning disabilities, neurological impairments, restricted growth, and organ harm, particularly affecting vulnerable children.
- Socioeconomic Ramifications: Lead poisoning contributes significantly to educational disparities between affluent and less affluent nations. Affected children often face hindrances in education and professional accomplishments, influencing the nation's overall productivity.
- Affected Regions: States like Bihar, Uttar Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh, Jharkhand, Chhattisgarh, and Andhra Pradesh contribute to around 40% of the population with elevated blood lead levels.
Factors Contributing to Lead Poisoning:
- Inadequate and Unregulated Recycling: The informal and substandard handling of lead-acid batteries in recycling processes.
- Vehicle Ownership Surge: The rise in vehicle ownership, coupled with the absence of proper regulation and infrastructure for recycling vehicle batteries.
- Hazardous Recycling Practices: Individuals engaged in risky and sometimes illegal recycling activities resort to breaking open battery casings, resulting in acid spills and lead dust contamination of the soil.

Government Measures to Mitigate Lead Poisoning:
- National Programme for Prevention and Control: In 2010, the National Programme for Prevention and Control of Fluorosis, Endemic Skeletal Fluorosis, and Arsenicosis was launched, with a focus on averting lead poisoning.
- Import Restrictions on Non-Compliant Lead Acid Batteries: The Ministry of Environment and Forests took action in 2013 by imposing a ban on the import of lead acid batteries that do not adhere to compliance standards.
- National Health Mission (NHM): The NHM plays a pivotal role by offering healthcare services, encompassing screening and treatment for lead poisoning.
- Regulation through Lead Battery Waste Management Rules, 2016: The implementation of these rules in 2016 has facilitated the proper disposal and safe recycling of lead-acid batteries.
- Targeted Healthcare via National Programme for the Health Care of the Elderly (NPHCE): With a specific focus on the elderly, who are more susceptible to lead poisoning, the NPHCE delivers essential healthcare services.
- Center for Advanced Research on Environmental Health (CAREH): CAREH, through its research endeavors in environmental health, contributes to understanding and addressing lead poisoning issues.
Global endeavors to combat lead poisoning have embraced diverse strategies:
- Gasoline Initiative (U.S.): The United States effectively curtailed blood lead levels by over 90% between 1976 and 1995 through the elimination of lead from gasoline.
- Regulations for Paint and Water Pipes: Numerous nations have implemented rigorous standards to ensure lead-free paints and water pipes, thus mitigating potential avenues of lead exposure.
- Bangladesh's Turmeric Approach: Bangladesh addressed lead contamination via turmeric adulteration by enforcing stringent regulations and boosting consumer awareness between 2017 and 2021. This effort resulted in a remarkable decline of lead-contaminated turmeric from 47% in 2019 to 0% in 2021.
Way Forward for India in Combating Lead Poisoning:
- Robust Legislative Framework– Establishing comprehensive legal provisions to set health and safety standards for products containing lead.
- Strengthen Regulation– Ensuring stringent enforcement of guidelines regarding lead-free paints and water pipes.
- Effective Monitoring System– Implementing a nationwide blood lead level testing initiative, including within household surveys to identify susceptible groups.
- Identification of Contaminated Zones– Conducting extensive searches for lead-contaminated areas across the country, with particular emphasis on addressing pollution near schools and residential areas.
- Advocate Sustainable Practices– Promoting the adoption of waste management and e-waste recycling initiatives to diminish lead contamination risks.
- Enhanced Inter-departmental Cooperation– Fostering collaborative efforts between governmental bodies, non-governmental organizations, and international collaborators to synchronize action.
- Public Awareness– Generating heightened awareness among parents, workers, educational institutions, and healthcare practitioners about the hazards of lead exposure.
Probable Questions for UPSC Mains Exam –
- Assess the magnitude of lead poisoning in India and its repercussions on health and education. Examine the contributing factors and propose policy actions for effective mitigation. (10 marks, 150 words)
- Evaluate global strategies to combat lead poisoning, citing instances. Discuss the role of legislation, inter-departmental collaboration, and public awareness in curbing lead exposure in India. (15 marks, 250 words)
Source – Indian Express